|
Broadband wavelength-swept Cr4+:YAG crystal fiber laser
Professor Sheng-Lung Huang
Graduate Institute of Photonics and Optoelectronics, National Taiwan University
臺灣大學光電所 黃升龍教授
We present a broadband wavelength-swept laser using a 16-μm-core-diameter Cr4+:YAG crystal fiber as the gain medium. The laser-diode-pumped crystal fiber laser has a threshold of only 102 mW due to the low propagation loss and high heat dissipation efficiency. The laser achieves a sweeping wavelength range of 134 nm, centered around 1425 nm, with a scanning speed of 163k nm/s. Notably, the cross-polarization-coupled excited state absorption of the signal wavelength constrained the long-wavelength lasing limit. This laser has the potential for swept source optical coherence tomography applications, providing an axial resolution of 11.4 μm.
|
|
|
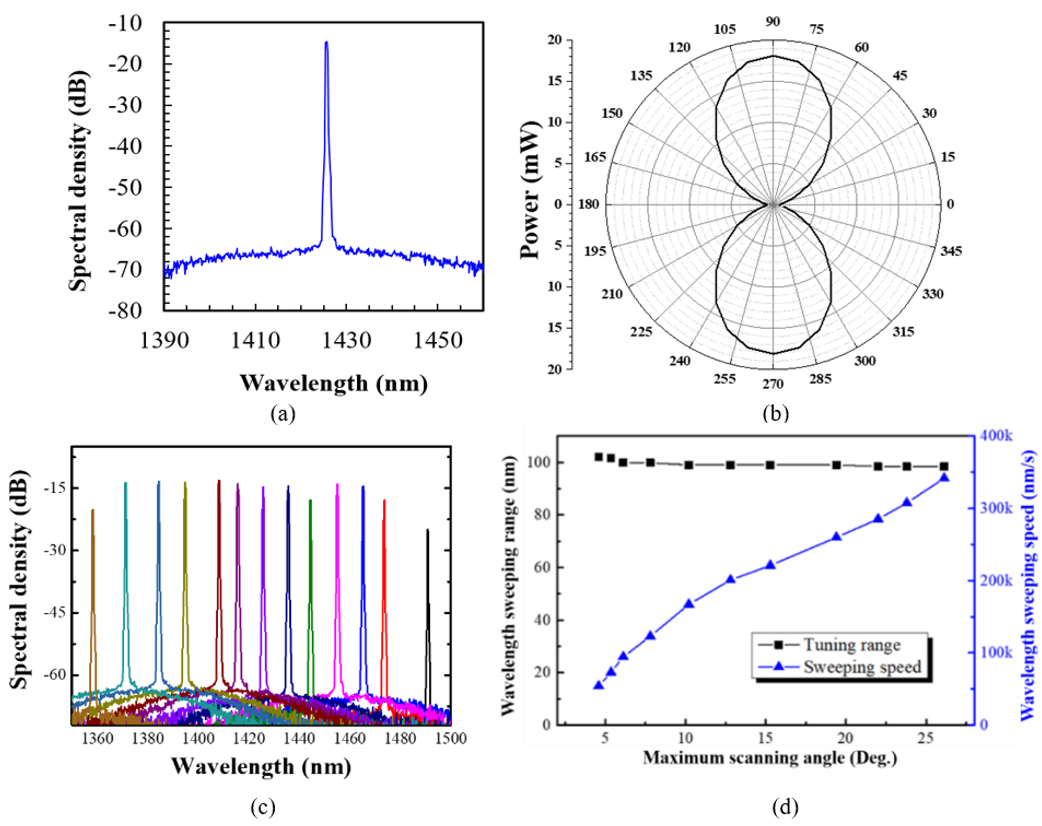
Fig. 1. The measured laser (a) instantaneous spectrum, (b) output polarization, and (c) tunable spectra from 1358 nm to 1491 nm. (d) Influence of wavelength sweep speed on the swept-laser wavelength range.
|
Reference:
Y. H. Li, Y. W. Lee, and S. L. Huang, "Broadband wavelength-swept Cr4+:YAG crystal fiber laser," Optics Express 31(20), pp. 32772–32782, 2023.
True-H&E Rapid Fresh Pathology Assisted with Mesoscale Nonlinear Optical Gigascope
Professor Chi-Kuang Sun
Graduate Institute of Photonics and Optoelectronics, National Taiwan University
臺灣大學光電所 孫啟光教授
Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E)-based frozen section (FS) pathology is presently the global standard for intraoperative tumor assessment (ITA). Preparation of frozen section is labor intensive, which might consume up-to 30 minutes, and is susceptible to freezing artifacts. An FS-alternative technique is thus necessary, which is sectioning-free, artifact-free, fast, accurate, and reliably deployable without machine learning and/or additional interpretation training.
Our team develop a training-free true-H&E Rapid Fresh digital-Pathology (the-RFP) technique which is 4 times faster than the conventional preparation of frozen sections. The-RFP is assisted by a mesoscale Nonlinear Optical Gigascope (mNLOG) platform with a streamlined rapid artifact-compensated 2D large-field mosaic-stitching (rac2D-LMS) approach. A sub-6-minute True-H&E Rapid whole-mount-Soft-Tissue Staining (the-RSTS) protocol is introduced for soft/frangible fresh brain specimens. The mNLOG platform utilizes third harmonic generation (THG) and two-photon excitation fluorescence (TPEF) signals from H and E dyes, respectively, to yield the-RFP images.
Our team demonstrate the-RFP technique on fresh excised human brain specimens. The-RFP enables optically-sectioned high-resolution 2D scanning and digital display of a 1 cm2 area in <120 seconds with 3.6 Gigapixels at a sustained effective throughput of >700 M bits/sec, with zero post-acquisition data/image processing. Training-free blind tests considering 50 normal and tumor-specific brain specimens obtained from 8 participants reveal 100% match to the respective formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE)-biopsy outcomes.
In conclusion, we provide a digital ITA solution: the-RFP, which is potentially a fast and reliable alternative to FS-pathology. With H&E-compatibility, the-RFP eliminates color- and morphology-specific additional interpretation training for a pathologist, and the-RFP-assessed specimen can reliably undergo FFPE-biopsy confirmation.
|