|
The Highly-efficiency 1.55-µm DFB laser with ns-level pulsed for LiDAR applications
Professor Chao-Hsin Wu
Graduate Institute of Photonics and Optoelectronics, National Taiwan University
台湾大学光电所 吴肇欣教授
Our team demonstrated a highly efficient 1.55 µm distributed feedback (DFB) laser diode. The optimized epitaxial structure resulted in a low threshold current of 12 mA and a high operating efficiency of 0.433 W/A. The laser exhibited stable single mode characteristics in both high bias current and wide temperature range testing. Additionally, the ns-level pulsed operation characteristics of the DFB laser were verified, achieving a pulse peak power of 6.27 W with a pulse optical width of 20.4 ns. The watt-level pulse optical power was achieved with a single active region. With its eye-safe wavelength, high operating efficiency, stable single-mode spectral characteristics, and high pulse optical power, the 1.55 µm DFB laser is a promising light source for ToF-based LiDAR systems.
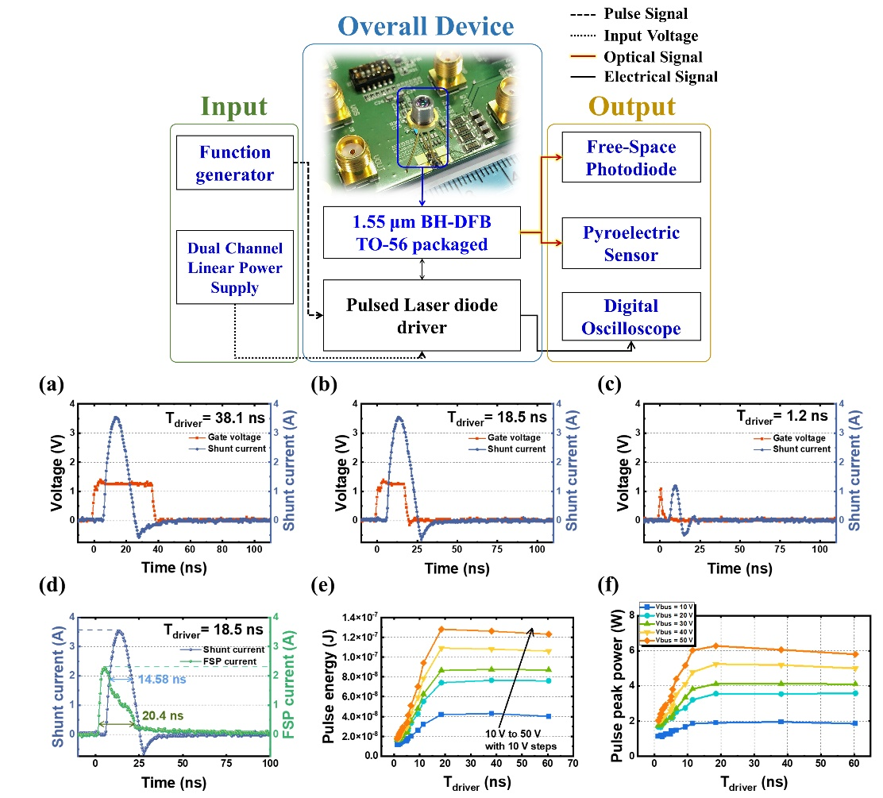
Under continuous-wave operation, the resistance is 3.17 ohm, and the optical power reaches 91 mW with a current of 0.3 A. In addition, the DFB laser displays excellent wavelength stability, maintaining an SMSR of over 33 dB even at high temperatures, thus ensuring stable single longitudinal mode operation. Then we estimate the pulse operation of the DFB laser using the narrow pulse generator. When Vbus is 50 V and Tdriver (pulse generator) is 18.5 ns, the experimental results show the time widths of the shunt current and optical signal are 14.58 and 20.4 ns, respectively. The pulse energy received by the pyroelectric sensor is 128 nJ, and the pulse peak power reaches up to 6.27 W.
This work has been published in Optics Letters: Te-Hua Liu, Hao-Tien Cheng, Jau-Yang Wu, and Chao-Hsin Wu*, "Achieving ns-level pulsed operation of up to 6.27 W with a 1.55-µm BH-DFB laser for LiDAR applications," Opt. Lett. 48, 3071-3074 (2023)
|
|
|
Fig. 1. (upper) Experimental configuration for ns-level short-pulse operation. (lower) (a) Electrical signal of the driver when Tdriver is 38.1 ns. (b) Electrical signal of the driver when Tdriver is 18.5 ns. (c) Electrical signal of the driver when Tdriver is 1.2 ns. (d) The oscilloscope monitors the shunt current and the optical signal of the FSP when Tdriver is set as 18.5 ns. (e) Comparison of the pulse energy received by the pyroelectric sensor under a range of Vbus and Tdriver parameters. (f) Comparison of the pulse peak power of the pulsed laser driver with the pulse width under different Vbus.
|
|