 |
|
 |
| |
|
發行人:吳育任所長 編輯委員:曾雪峰教授 主編:林筱文 發行日期:2023.10.30
|
| |
|
 |
|
 本所吳育任教授及法國國家科學研究中心(CNRS)Marcel Filoche研究主任合作團隊榮獲
「2023年第25屆臺法科技獎
」,特此恭賀!
本所吳育任教授及法國國家科學研究中心(CNRS)Marcel Filoche研究主任合作團隊榮獲
「2023年第25屆臺法科技獎
」,特此恭賀!
 本所吳肇欣教授榮膺「2024 Optica(前美國光學學會, OSA)Fellow」,特此恭賀!
本所吳肇欣教授榮膺「2024 Optica(前美國光學學會, OSA)Fellow」,特此恭賀!
本所11月份演講公告:
| 日期 |
講者 |
講題 |
地點 |
時間 |
| 11/10 |
王蒞君教授
國立陽明交通大學電機工程學系 |
Exploring 6G Base Stations Technologies for Future Resilient, Sustainable, and Eco-Friendly Smart City |
博理館
101演講廳 |
14:20~16:00 |
| 11/17 |
劉舜維教授
明志科技大學電子系 |
待定 |
博理館
101演講廳 |
14:20~16:00 |
|
|
|
|

|
|

|
|
| |
|
|

|
|
9月份「光電所專題演講」(整理:簡璟)
|
|
時間:
|
112年9月8日(星期五)下午3時
|
|
講者:
|
Prof. Sabina Merlo (Department of Electrical, Computer and Biomedical Engineering, University of Pavia, Italy)
|
|
講題:
|
Electromechanical characterization of M(O)EMS by spot optical interferometric techniques
|
|
|
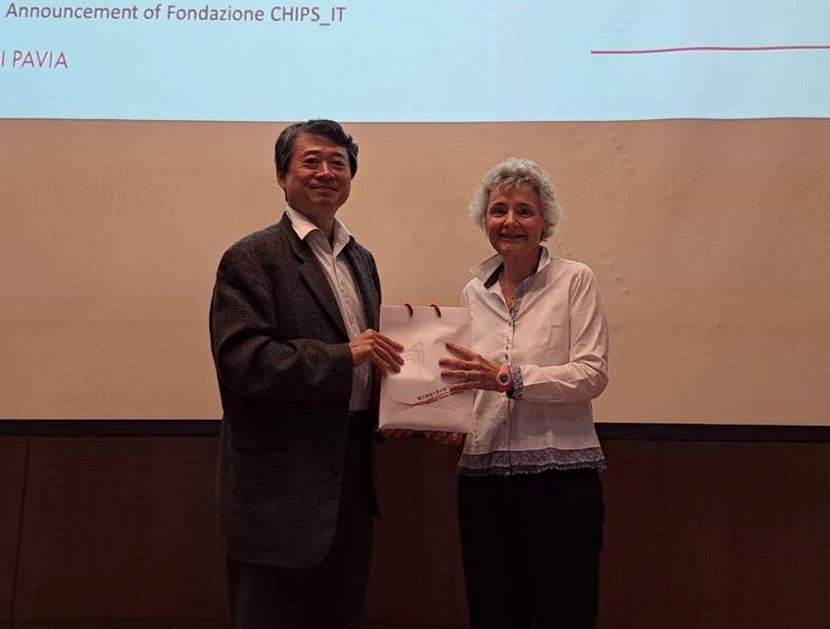

|
|
Prof. Sabina Merlo(右)與本所黃升龍教授(左)合影
|
|
|
時間:
|
112年9月22日(星期五)下午2時20分
|
|
講者:
|
林子茗學輔專員(國立臺灣大學學務處學輔中心)
|
|
講題:
|
研究生生存指南—與壓力共處
|
|
|
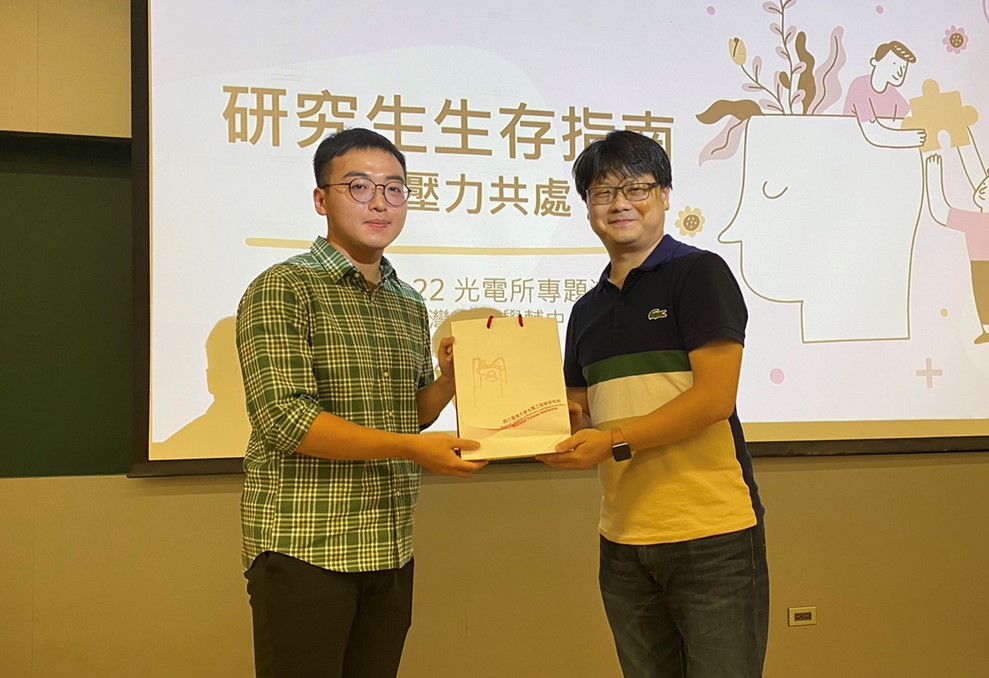

|
|
林子茗學輔專員(左)與本所李翔傑教授(右)合影
|
|
|
10月份「光電所專題演講」
(整理:簡璟)
|
|
時間:
|
112年10月6日(星期五)下午2時20分
|
|
講者:
|
葉秩光教授(國立清華大學生醫工程與環境科學系)
|
|
講題:
|
Acoustic vortex for confining light fluence
|
|
|
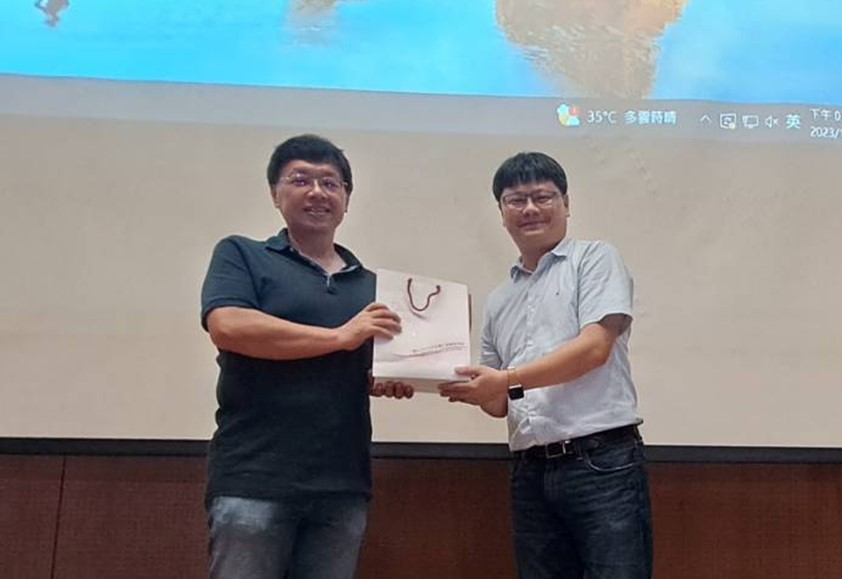

|
|
葉秩光教授(左)與本所李翔傑教授(右)合影
|
|
|
時間:
|
112年10月13日(星期五)下午2時20分
|
|
講者:
|
陳隆建教授(國立臺北科技大學光電工程學系)
|
|
講題:
|
Progress of all-inorganic perovskite quantum dot light-emitting diodes
|
|
|
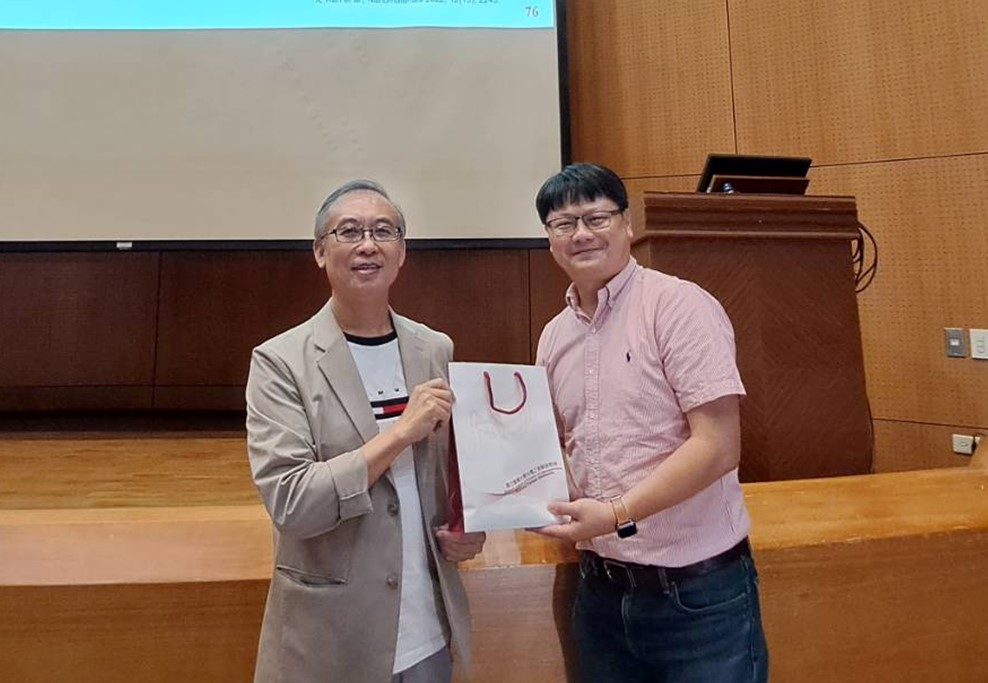

|
|
陳隆建教授(左)與本所李翔傑教授(右)合影
|
|
|
時間:
|
112年10月20日(星期五)下午2時20分
|
|
講者:
|
林曉均教授(國立清華大學生醫工程與環境科學系)
|
|
講題:
|
Light and Sound: Biomedical Optoacoustic Imaging
|
|
|

|
|
林曉均教授(右)與本所李翔傑教授(左)合影
|
|
|
時間:
|
112年10月27日(星期五)下午2時20分
|
|
講者:
|
王萬倉處長(友達光電前瞻技術中心)
|
|
講題:
|
Flexible Technology Evolution: from Rigid to Flexible, and Beyond
|
|
|

|
|
王萬倉處長(右)與本所李君浩教授(左)合影
|
|
|
|
|

|
|

|
|
| |
|
|

|
|
Manipulation of plasmonic relaxation possible by voltage-modulation
Professor Jian-Jang Huang's Laboratory
Graduate Institute of Photonics and Optoelectronics, National Taiwan University
臺灣大學光電所 黃建璋教授
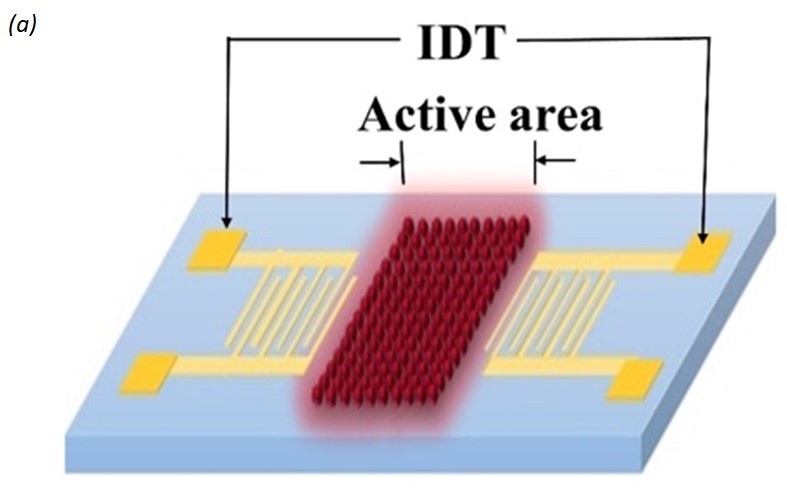
We experimentally study the effect of amplitude varying surface acoustic waves on localized surface Plasmon (LSP), which unveils exceptional properties of plasmon-phonon interaction with promising applications in future tunable photonic devices. Gold nanoparticles are deposited on an X-cut LiNbO3 to generate plasmonic oscillation, and an interdigital transducer is fabricated to create surface acoustic wave pulses. The interaction between amplitude varying mechanical wave and plasmonic oscillation affects different plasmon dynamics and relaxation gradients, leading to a systematic change in LSP absorption. We also demonstrated the effect of polarized light on the device, providing a unique characteristic to explore the manipulation process effectively.
|
|
|
|
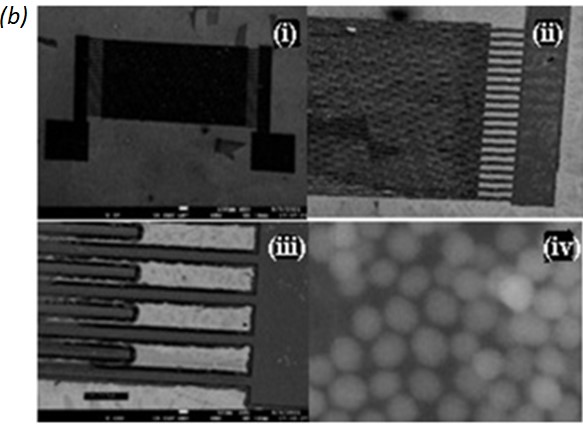
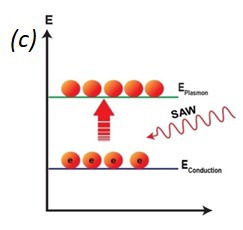
Fig. 1. (a) Illustration of the device, which is composed of a source IDT, randomly distributed Au nanoparticles and a receiving IDT. (b) (i) (ii) (iii) SEM images of fabricated IDT, (iv) Surface morphology captured by SEM where 40nm uniformly sized Au nanoparticles are distributed on the surface.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
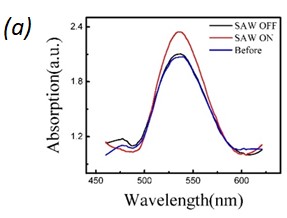
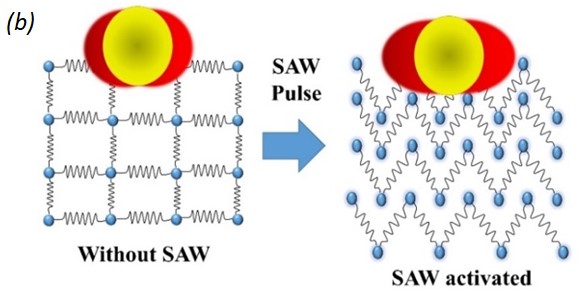
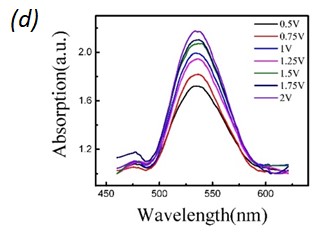
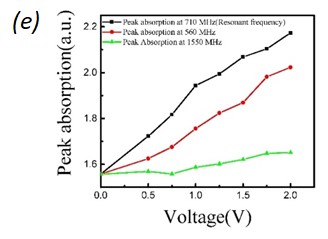
Fig. 2. (a) LSPR response with respect to different switching conditions of the IDT. Where the LSPR adsorption increase with SAW is On and retract back when SAW is off. (b) Diagram of phonon-plasmon interaction with and without SAW activated acoustic phonons. The plasmonic electron density increases with the applied SAW pulse as compared to the case without SAW. (c) Illustration of SAW activated electron transition to the plasmonic state. The SAW activated phonons participate in phonon-plasmon coupling and increase the plasmonic population. (d) Change of LSPR absorption with varying amplitude of SAW. (e) Amplitude varying LSPR response with respect to different SAW resonant conditions, where at the SAW resonant frequency (710 MHz) the change of LSPR absorption is highest.
|
Low-Temperature HfZrO2 Ferroelectric Thin-Film Transistors with a-InGaZnO Channels
Professor I-Chun Cheng
Graduate Institute of Photonics and Optoelectronics, National Taiwan University
臺灣大學光電所 陳奕君教授
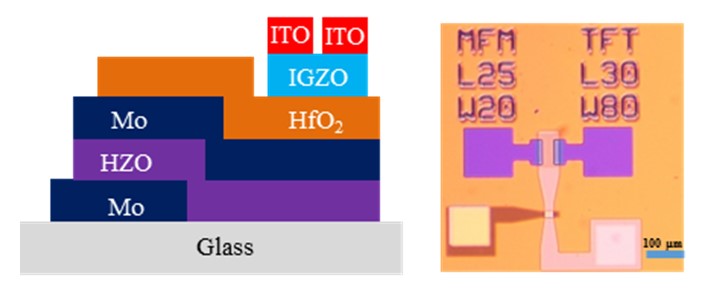
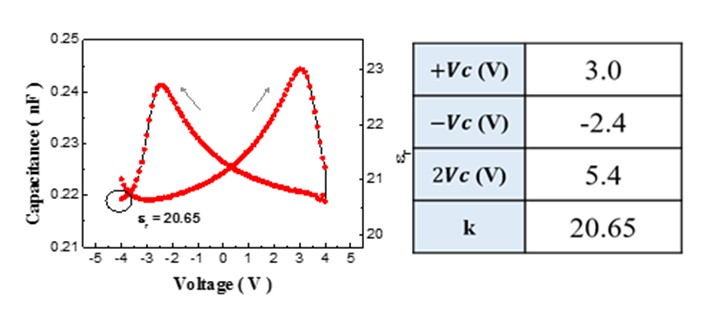
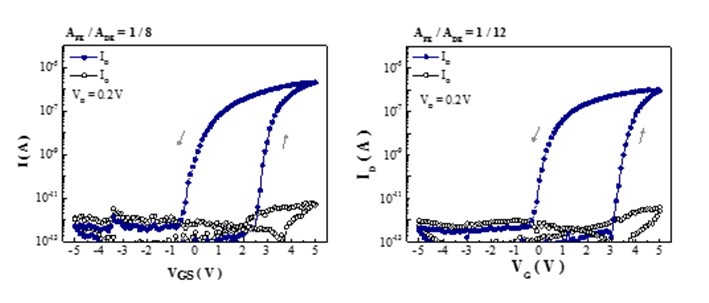
Owing to the relatively low process temperatures, HfO2-based ferroelectric materials integrated with oxide-based thin-film transistors have been considered as potential candidates for back-end-of-line compatible ferroelectric field-effect transistors, which can be vertically stacked on silicon CMOS circuits to realize high-density neural network applications or implemented on various types of substrates for novel applications. It is known that the formation of ferroelectric orthorhombic phase in HfO2-based materials can be strongly influenced by the annealing temperature, the thickness of film and the types of top and bottom metallic electrodes. In this work, low-temperature ferroelectric thin-film transistors (Fe-TFTs) were developed by monolithically integrating HfZrO2 (HZO) ferroelectric capacitors with amorphous indium gallium zinc oxide (a-IGZO) TFTs on glass substrates. Figs. 1(a) and (b) show the schematic diagram and microscopic photograph of the on-glass FeTFT, respectively. The Fe-TFT has a metal-ferroelectric-metal-insulator-semiconductor structure. The HZO ferroelectric layer was deposited by atomic layer deposition. The a-IGZO channel layer was deposited by rf-sputtering. The maximum process temperature is 350°C. A butterfly-shaped capacitance-voltage curve is observed, as shown in Fig. 2, revealing the top and bottom Mo electrodes can introduce sufficient mechanical stress to induce the formation of ferroelectricity in the HZO layer after annealed at 350°C. The positive and negative coercive voltages are 3 V and -2.4 V, respectively. The dielectric constant is 20.65. Fig. 3 shows the transfer hysteresis curves of the low-temperature HZO Fe-TFTs. The Fe-TFTs exhibit large hysteresis memory windows of 2.8 V and 3.8 V when the area ratios between ferroelectric capacitors and gate insulators are 1/8 and 1/12, respectively.
|
|
|
|
Fig. 1. (a) Schematic diagram and (b) optical micrograph of HZO Fe-TFT with a-IGZO channel.
|
Fig. 2. Capacitance-voltage curve & dielectric constant of low-temperature annealed HZO ferroelectric capacitor.
|
|
|
|
Fig. 3. Transfer hysteresis curves of HZO FeTFTs with (a) AFE / ADE = 1 / 8 and (b) AFE / ADE = 1 / 12. The Fe-TFTs are operated at VDS = 0.2 V.
|
|
|
|
|

|
|

|
|
| |
|
|

|
|
論文題目:適用於系統以及電路模擬的異質介面雙載子發光電晶體模型
姓名:楊順 指導教授:吳肇欣教授
|
摘要
|
|
異質結雙極發光電晶體(也稱為 LET 和 HBLET),基於量子井的異質結雙極發光晶體管由於其具有多端口操作能力,因此能夠作為光通信和光電集成電路(OEIC)中的候選器件。
從器件物理開始,我們構建了發光電晶體模型,用於光電集成電路和電氣設計自動化的仿真和使用。除了對器件功能很重要的發光電晶體基本特性之外,我們的模型還準確描述了發光電晶體的電到電和電到光特性。還提供導納矩陣,用於調製響應的通用模擬,包括散射參數和電流增益。為了確保電路模擬器SPICE兼容,還給出了發光電晶體的大信號眼圖。在我們的模型的幫助下,可以加快電路設計的過程,這也可以幫助電路設計者分析自己電路的有效性。
本篇論文並模擬比較發光電晶體在熱感應器,光收發器的效能。另外也運用TCAD模擬元件内部電流以及載子複合的分佈,以及不同尺寸下的元件跟電路特性。
 |
 |
|
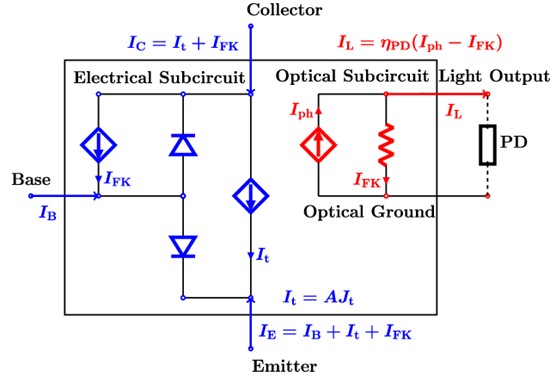
圖一、發光電光晶體等效電路
|
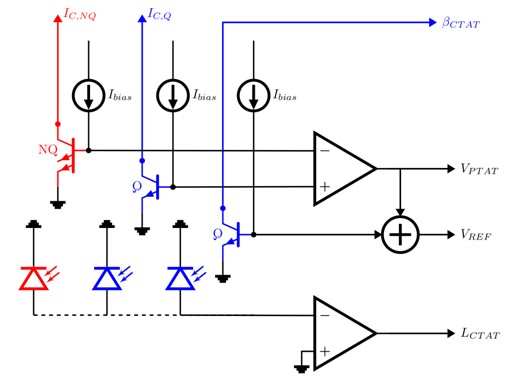
圖二、發光電晶體多模態熱感應電路
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|

|
|
| |
|
|

|
|
— 資料提供:影像顯示科技知識平台 (DTKP, Display Technology Knowledge Platform) —
— 整理:林晃巖教授、林珈慶 —
晶片上的微波震盪器
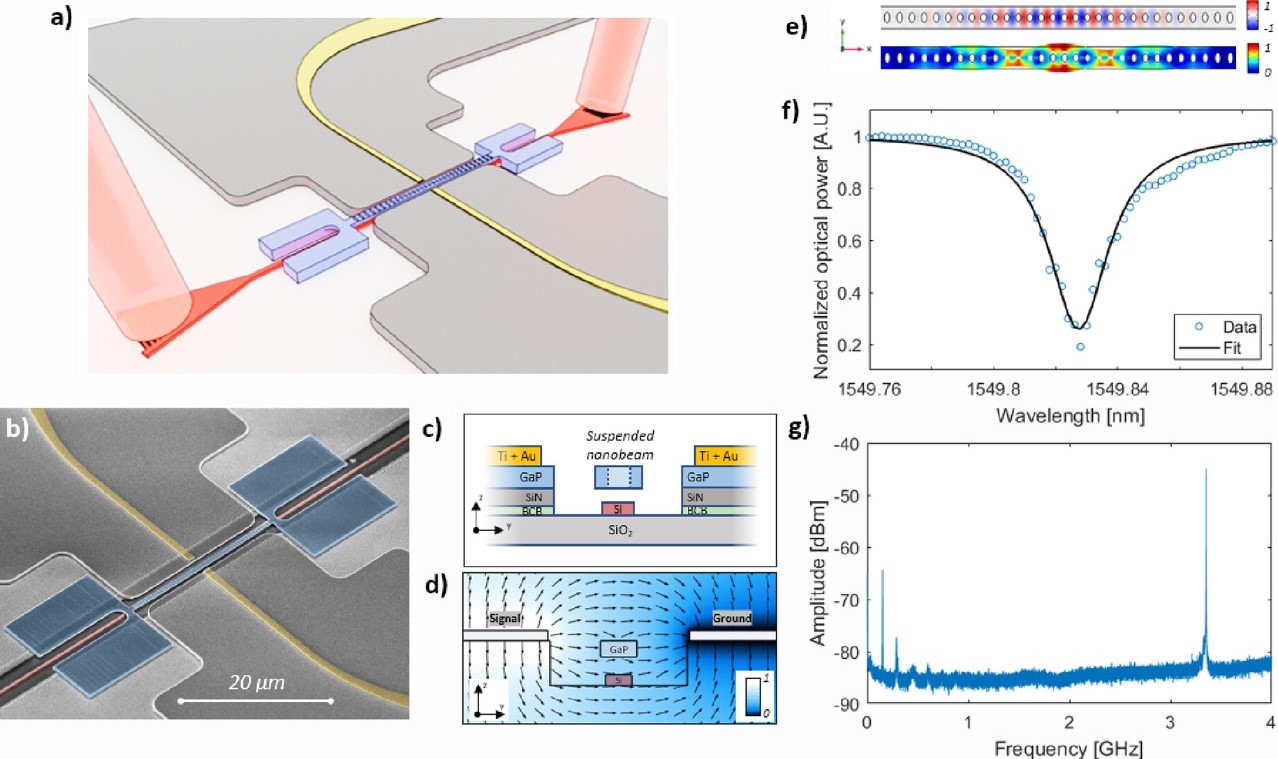
最新研究指出,光學晶片可能成為純凈、低噪音微波信號之有前途的整合來源,適用於衛星通信和5G行動網路的應用。來自巴黎Saclay大學和法國公司Thales的Róbert Hórvath及其同事們在實驗中證明,由光激發的磷化鎵懸浮奈米橫樑可在3.35 GHz的頻率下作為高性能振盪器(Róbert Hórvath, et al.,” Sub-Hz Closed-Loop Electro-Optomechanical Oscillator with Gallium Phosphide Photonic Crystal Integrated on SoI Circuitry,” ACS Photonics, 2023)。特別是,該來源在尺寸為30 × 0.7 μm2的晶片上具有約0.7 Hz的線寬和約–111 dBc Hz-1的相位噪音。
這個集成在絕緣體上矽之光學電路上的鎵磷化物(GaP)奈米橫樑,經過精心設計的孔洞模式,使其成為一個一維光子晶體腔。這個腔體具有強烈的光機耦合,可以有效地限制光學模態和千兆赫機械模態。當以1,550 nm的共振波長的光透過光學波導被注入腔體時,它會激發腔體的機械模態,這種模態會對光學信號進行調變,並有效地被印刻在信號上。隨後,光學信號從腔體中送出,然後由連接到光電二極體的電譜分析儀進行檢測,清楚地顯示在3.35 GHz處有一個單一而尖銳的峰值。
|
|
|
圖一、在絕緣體上矽之光學電路上製作鎵磷化物(GaP)奈米橫樑,成為一個一維光子晶體腔。(a) 元件示意圖;(b) 元件照片;(c) 剖面圖;(d)(e) 場圖;(f)(g) 頻譜圖。
|
參與該研究的研究人員之一Rémy Braive評論道:「我們的設計結合了III-V族材料在電光機械方面的優勢和矽平台在可製造性和集成性方面的優點,此外,與其他微波振盪器相比,它的佔用空間小,耗能低。」
進一步的功能是透過使用在晶片上的金電極引入的,這些電極分別位於鎵磷化物(GaP)奈米橫樑的兩側,相距1μm,當施加電壓於橫樑上時,可以在橫樑長度的垂直方向上創造一個橫向的電場。由於鎵磷化物具有壓電性,施加的電場可以直接引入電機耦合作用,以幫助調整設備的響應。為了提高振盪的品質,法國研究團隊實施了一個電光閉環反饋迴路,其中包括一段長度為210米的光纖作為延遲線,以及應用於電極的射頻信號。Braive解釋道:「我們未來的計劃是使用聲子相對於光子的緩慢傳播的特性,在晶片上集成延遲線。」
|
參考資料:
|
Graydon, O., "Microwave oscillator on a chip," Nature Photonics 17, pages 648 (2023)
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-023-01259-0
DOI:10.1038/s41566-023-01259-0
|
|
參考文獻:
|
Róbert Hórvath, et al., "Sub-Hz Closed-Loop Electro-Optomechanical Oscillator with Gallium Phosphide Photonic Crystal Integrated on SoI Circuitry," ACS Photonics 10, No. 8, pages
2540–2548 (2023)
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsphotonics.3c00074
DOI:10.1021/acsphotonics.3c00074
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|

|
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
|