|
|
 |
|
 |
| |
发行人:黄建璋所长 编辑委员:曾雪峰教授 主编:林筱文 发行日期:2022.02.28 |
| |
|
 |
|

本所苏国栋教授指导硕士生刘思彤同学荣获「2022年物理年会墙报论文优等奖」,特此恭贺!
墙报论文名称:Heterodyne Sum-Frequency Surface Phonon Spectroscopy
|
|
 |
|
 |
|
| |
|
 |
|
10月份「光电所专题演讲」(整理:姚力琪) |
|
时间: |
2021年10月1日(星期五)下午2时20分 |
|
讲者: |
张鼎张讲座教授(国立中山大学物理系) |
|
讲题: |
低温缺陷钝化技术在半导体组件应用 |
|
 |
|
张鼎张教授(左)与本所所长黄建璋教授(右)合影 |
|
|
时间: |
2021年10月15日(星期五)下午2时20分
〈※
在线演讲〉 |
|
讲者: |
陈阶晓执行长(钛隼生物科技股份有限公司) |
|
讲题: |
Robots in OR, the Future is NOW |
|
|
|
|
时间: |
2021年10月22日(星期五)下午2时20分 |
|
讲者: |
陈启东博士(中央研究院物理研究所) |
|
讲题: |
Building a Superconducting Quantum Computer |
|
|
|
11月份「光电所专题演讲」(整理:姚力琪) |
|
时间: |
2021年11月5日(星期五)下午2时20分 |
|
讲者: |
陈冠能讲座教授(国立阳明交通大学电子研究所) |
|
讲题: |
3D IC and Advanced Packaging |
|
 |
|
陈冠能教授(右)与本所所长黄建璋教授(左)合影 |
|
|
时间: |
2021年11月12日(星期五)下午2时20分
〈※
在线演讲〉 |
|
讲者: |
曲建仲博士(知识力科技股份有限公司 (Ansforce Inc.) 执行长兼科技顾问) |
|
讲题: |
晶圆代工与先进封装技术应用商机 |
|
|
|
时间: |
2021年11月19日(星期五)下午2时20分
〈※
在线演讲〉 |
|
讲者: |
徐茂修博士(敦泰电子股份有限公司) |
|
讲题: |
高速传输整合声音、影像、数据、电力传输之方案IC设计 |
|
|
|
12月份「光电所专题演讲」(整理:姚力琪) |
|
时间: |
2021年12月10日(星期五)下午2时20分
〈※
在线演讲〉 |
|
讲者: |
吴文中教授(国立台湾大学工程科学及海洋工程学系) |
|
讲题: |
My IoT Journey. From research, startup to tech jobs. |
|
|
|
时间: |
2021年12月17日(星期五)下午2时20分
〈※
在线演讲〉 |
|
讲者: |
萧立人博士(国家中山科学研究院) |
|
讲题: |
Beyond the Lab 课外研究 |
|
|
|
1月份「光电所专题演讲」(整理:姚力琪) |
|
时间: |
2022年1月14日(星期五)下午2时20分
〈※
在线演讲〉 |
|
讲者: |
谢承哲先生(IBM Infrastructure specialist) |
|
讲题: |
职涯转换的权衡与经验 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
|
| |
|
 |
Coherent Tri-mode FPLD with SCM of 80 Gbit/s OFDM for 75-km Long-Reach MMWoF at 28 GHz
Professor Gong-Ru Lin’s Laboratory
Graduate Institute of Photonics and
Optoelectronics, National Taiwan University
台湾大学光电所 林恭如教授
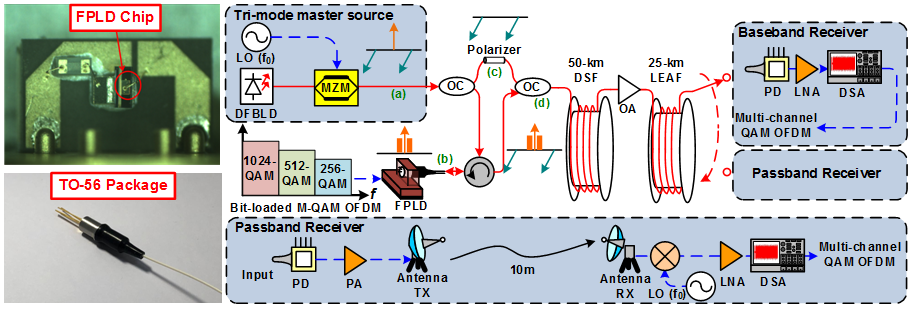
A novel FPLD with orthogonal polarized tri-mode under single-carrier modulation (SCM) for chromatic dispersion suppression is employed to demonstrate 28-GHz remote optical heterodyne in millimeter-wave-carrier-over-fiber (MMWoF) for 75-km long-reach wireline and wireless transmission at 80 and 30 Gbit/s under bit-loaded M-QAM OFDM with spectral usage efficiency up to 10 bit/s/Hz. The 28-GHz and 75-km long-reach MMWoF constructed by an orthogonal tri-mode LD with SCM is exhibited in Fig. 1. A single-polarization light source generated from a DFBLD was adjusted a 45o polarization between the light source and the Mach-Zehnder modulator (MZM). A 28-GHz LO sinusoidal wave was modulated onto the single-polarization light source by a MZM with null-point operation for the orthogonal tri-mode master source generation (point (a)). The orthogonal tri-mode master was divided into two paths by an optical coupler. One path of this master source injection-locked a Fabry-Perot LD (FPLD) only supporting the TE polarization. The side modes of the tri-mode source with the TM polarization would be suppressed in the FPLD cavity, which implements the SCM (point (b)). For another path, the central carrier of the tri-mode source was suppressed by a polarizer (node (c)). The injection-locked carrier and central-carrier suppressed side-modes source were orthogonal combined by another optical coupler to form an orthogonal tri-mode optical carrier with SCM (point (d)). The narrow-band 64- to 1024-QAM OFDM with the bandwidth from 166 to 100 MHz was generated by an 18-GSa/s AWG. The bit-loaded QAM-OFDM data was modulated on the injection-locked carrier with side-mode suppression by the FPLD as an optical amplifier and modulator.
|
|
|
Fig. 1. The microscopic image, package photo, and network scheme of a tri-mode FPLD with SCM of M-QAM OFDM for 75-km long-reach MMWoF. |
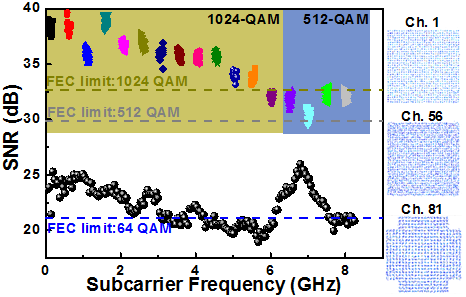
To maximize the transmission capacity and meet the 5G standard, the multi-channel bit-loaded M-QAM OFDM with 100-MHz/channel bandwidth is employed. The maximal channel number in 8-GHz bandwidth is obtained as 80, and the first channel is set from 70 MHz. After demodulation, the SNR spectra of each narrow-band bit-loaded M-QAM OFDM data and the wide-band 64-QAM OFDM data delivered by orthogonal tri-mode optical carrier after 75-km transmission are exhibited in Fig. 2. Figure
3 also shows the related constellation plots for the narrow-band bit-loaded M-QAM OFDM data. The maximal bandwidth and raw data rate of the delivered wide-band 64-QAM OFDM, which can pass the FEC limit, are obtained as 8 GHz and 48 Gbit/s, respectively. For the narrow-band case, the total raw data rate of the delivered multi-channel bit-loaded M-QAM OFDM data is evaluated as 10 (1024 QAM)
x6 GHz+9 (512 QAM) x2.2 GHz=80 Gbit/s.
|
|
|
Fig. 2. The SNR spectra of narrow-band M-QAM OFDM data and wide-band 64-QAM OFDM data delivered by orthogonal tri-mode optical carrier after 75-km transmission. |
|
 |
|
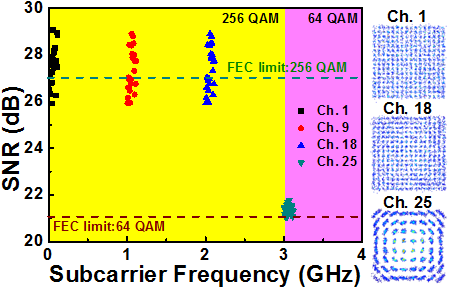
Fig. 3. The frequency spectra of the delivered multi-channel M-QAM OFDM by beat 28-GHz MMW carrier after 10-m free space transmission. |
The multi-channel bit-loaded M-QAM OFDM data with the same channel bandwidth is also employed at wireless transmission. After the same demodulation, the SNR spectra of each narrow-band M-QAM OFDM data with the related constellation plots are exhibited in Fig. 3. The SNR of the 1st channel is measured as 27.2 dB to pass the 256-QAM FEC limitation with a BER of 3.1x10-3 and an EVM of 4.4%. When increasing the channel to 25, the SNR is degraded to 22.5 dB, which can also pass the 64-QAM FEC limitation with a BER of 1.1x10-3 and an EVM of 7.5%. Therefore, the total raw data rate of the delivered multi-channel bit-loaded M-QAM OFDM data is evaluated as 8 (256 QAM)
x3 GHz+6 (64 QAM) x1 GHz=30 Gbit/s.
Minority Carrier Decay Length Extraction from Scanning Photocurrent Profiles in Two-Dimensional Carrier Transport Structures
Professor Ming-Hua Mao’s Laboratory
Graduate Institute of Photonics and
Optoelectronics, National Taiwan University
台湾大学光电所 毛明华教授
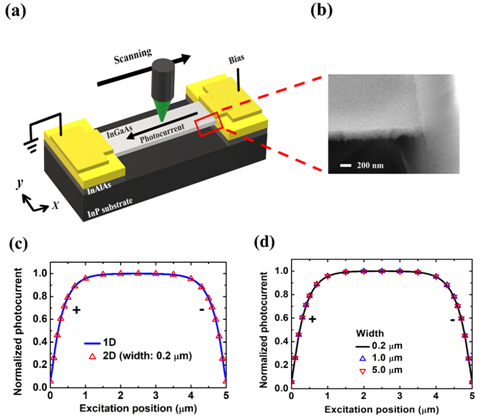
Carrier transport was studied both numerically and experimentally using scanning photocurrent microscopy (SPCM) in two-dimensional (2D) transport structures, where the structure size in the third dimension is much smaller than the diffusion length and electrodes cover the whole terminal on both sides. The scanning photocurrent simulation results surprisingly showed almost identical profiles from structures with different widths. The simulation results indicate that the integrated carrier distribution in the 2D transport structures with finite width can be well described by a simple-exponential-decay function with the carrier decay length as the fitting parameter, just like in the 1D transport structures. Furthermore, our simulation results demonstrate that the scanning photocurrent profiles in the ohmic- or Schottky-contact three-dimensional (3D) transport structures with electrodes covering the whole terminal on both sides will reduce to those described by the corresponding 1D fitting formulae. Finally, experimental SPCM on a p-type InGaAs
air-bridge two-terminal thin-film device was carried out. This study allows us
to extract the minority carrier decay length and to obtain the mobility-lifetime
product which can be used to evaluate the performance of 2D carrier transport
devices. This work has been published in
Scientific Reports:
Yu‑Chien Wei, Cheng‑Hao Chu, and Ming‑Hua
Mao*, “Minority Carrier Decay Length Extraction from Scanning Photocurrent
Profiles in Two-Dimensional Carrier Transport Structures,”
Scientific Reports,
11, 21863, (2021).
|
|
|
Fig. 1. (a) Schematic of the SPCM setup in an InGaAs air-bridge two-terminal thin-film device. (b) SEM images for one side of the measured InGaAs air-bridge two-terminal thin-film device. (c) Scanning photocurrent profile of the 0.2 μm wide case compared with that of the 1D transport structure. (d) Scanning photocurrent profiles with different widths. |
|
 |
| |
|
|
|
 |
|
| |
|
 |
论文题目:可见光氮化镓超颖透镜之研究
姓名:陈孟忻
指导教授:林晃岩教授
| 摘要 |
|
超颖透镜是超颖表面开发中最重要的应用之一。目前各式各样的材料已被应用于制作超颖透镜,使其在某些特定频带中达到高效率与低制造成本的需求。在这些材料中,考虑材料的各项优点,尤其是在半导体制造的量产能力,宽能隙氮化镓属最具潜力的材料之一。在本论文中,氮化镓被选为制造在可见光波段工作的高性能超颖透镜的关键材料,而其超颖透镜的设计原理乃基于几何相位或传播相位之概念。
几何相位设计的超颖透镜需要圆偏振平面波作为入射光,实验结果在405、532与633奈米之可见光波长下,其绕射极限聚焦效率分别高达79%、84%和89%。另一方面,以传播相位设计之超颖透镜具偏振方向不敏感之特性,得以聚焦任意线性偏振方向之入射光。经实验证明这些具偏振方向不敏感的超颖透镜在405、532与633奈米之三个不同波长下,其绕射极限聚焦效率分别为93%、86%和92%。
在实际应用方面,本论文提出一个开创性的概念,即透过超颖透镜检测发光二极管的图案化蓝宝石基板。为了实施概念验证,分别选择不具有磊晶层以及具有磊晶层的市售图案化蓝宝石基板作为待检测物,以执行超颖透镜的检测能力。透过适当选择所需波长所设计的超颖透镜,可以在图中清楚地观察到图案化蓝宝石基板中结构的顶点。
本研究为以宽能隙氮化镓制作的超颖表面之应用展现了一道曙光。预计在不久的将来,超薄氮化镓超颖透镜将取代厚重的光学组件,成为未来光学的主流。
|
 |
|
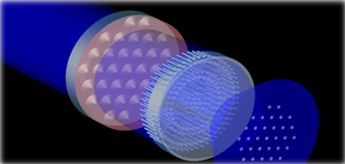
图一、透过超颖透镜检测图案化蓝宝石基板示意图 |
|
 |
|
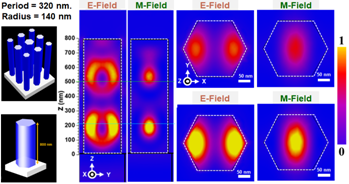
图二、超颖透镜排列方式以及单根柱对应之模拟电场磁场侧视与俯视强度分布图 |
|
|
 |
|
 |
|
| |
|
 |
— 资料提供:影像显示科技知识平台 (DTKP, Display Technology
Knowledge Platform) —
—
整理:林晃岩教授、吴思洁 —
受金属有机框架保护的钙钛矿
高亮度发光体的发展是实现下一代高清显示器的关键。负责视频广播技术标准的联合国机构-国际电信单位(International Telecommunication Unit, ITU),提出1000至10000 cd m-2高亮度(BT.2020或Rec. 2020)用于超高清屏幕市场终端系统输出。
钙钛矿发光二极管(Perovskite light-emitting diodes, PeLED)是未来显示器的潜在候选者,因为它们与基于低成本的溶液制程具有兼容性,同时具有出色的色彩质量。 PeLED 提供最大的亮度水平达到104 cd m–2(参考文献1, 2)的数量级,原则上满足BT.2020的亮度表现,但没有系统损耗的余地。钙钛矿奈米晶体(Perovskite nanocrystals, PeNCs)是出色的发射器,因为它们具有高色彩纯度,这源于窄的发射光谱,其半高全宽(FWHM)为20 nm。此外,通过控制成分,特别是卤素含量,可以方便地调整PeNC发射的颜色。结果是,使用PeLED应该可以实现比传统有机LED具有更宽色域的显示器,传统有机LED由于其振动耦合(vibronic coupling)而具有宽带发射光谱。值得注意的是,钙钛矿奈米晶体LED也已实现,其操作效率超过20%(参考文献2)。
然而,目前即使在100 cd m-2数量级的低亮度水平下运行时,PeLED的工作寿命通常也仅限于几分钟到几小时,与BT.2020中的ITU最小值相差一个数量级。迄今为止,在低亮度级别,所量测到最佳工作时间达到数百小时(在500 cd m-2下大约为300小时)[3],同时更高的工作亮度下组件寿命呈现指数下降。主要问题常见于PeNCs在薄膜中本质上是不稳定的。PeNCs通常会降解为体相(bulk phase)。特别是在运行期间施加在器件上的电场的影响下,离子迁移占主导地位,这被视为主动器件条件下PeNC寿命短的最主要原因。因此,在主动LED中保持PeNC稳定使达到高亮度水平是实现BT.2020兼容性的主要挑战。
现在报导在Nature Photonics中,Tsai及其团队使用金属有机框架(metal–organic frameworks, MOF)来稳定发光薄膜中的PeNC[4]。结果是LED的电驱动活性层(图1a)避免了离子迁移以及合并到体相的问题,同时提供了令人印象深刻的最大亮度水平超过105 cd m-2。
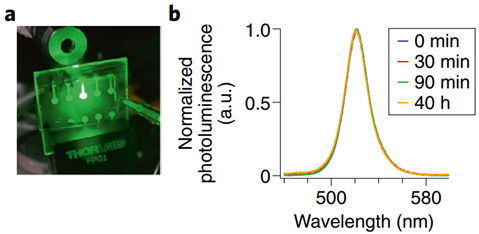
作者在介孔Pb-MOF矩阵结构中原位获得了具有约8 nm和13 nm双尺寸分布的发射性甲基铵三溴化铅 (MAPbBr3) 奈米晶体,该矩阵结构预先建构为基板上的三维(3D)网络化薄膜。最终转换的Pe-MOF结构在其产生的LED运行期间和之后持续显示一个FWHM约为20 nm的出光发射(图1b)。这种MOF稳定的MAPbBr3奈米晶体LED 达到120,000 cd m-2 的亮度水平,这是绿色光谱范围内的一个显著水平。当在5000 cd m–2 的初始亮度水平(在 BT.2020 范围内)下运行时,T50寿命(电激发光强度水平值减半的运行时间)量测为8.3个运行小时,并且在初始亮度150 cd m-2运行时间有40小时。在设备运行之后,PeNC 被证明完全没有离子迁移或任何降解(图1b)。这一项成就是未来为BT.2020兼容寿命长且明亮显示器生产MOF稳定的PeNC LED的一个重要里程碑。
|
|
|
图1、MOF PeNC LED。 a. 运行中MOF稳定的PeNC LED。 b. 以电驱动LED数小时后PeNC的光激发光光谱。发现发射光谱在发射峰值和光谱宽度上都没有变化。 |
在寻求稳定的PeNC的过程中,必须防止离子迁移以实现长期稳定性,因为它会导致组件性能不可恢复的衰退。为了稳定PeNC,各种不同的策略被报导,包括使用添加剂进行钝化、掺杂、配体工程(ligand engineering)和调整奈米晶体的核壳结构。 MOFs以前也被用作PeNCs的宿主矩阵结构,以提高其稳定性[5-9]。然而,这些早期研究的重点并不是电驱动的发光薄膜。这里的技术挑战是沉积均匀的电激发光薄膜以制造优质LED,同时保持足够的导电性以有效地注入电荷。关键的控制参数是前体(precursor)的浓度和薄膜厚度,以平衡薄膜中形成的发射中心的数量和将电荷均匀注入薄膜的能力。Tsai等人将Pe-MOF结构优化至210 nm的膜厚。
制作均匀的发光薄膜对于制造高性能LED非常重要。要建构均匀的发射层,首先需要构建具有良好均匀性和覆盖范围的MOF网络。MOF通常在有机溶剂中的溶解性较差,这阻碍了在薄膜上形成均匀的3D MOF结构。为了解决这个问题,会加入酸来仔细调整pH值,将MOF溶解成透明溶液进行旋涂(旋转涂布,spin-coat)。然后旋涂Pb-MOF薄膜以构建3D介孔结构,将Pb与羧基(carboxylic)有机桥连接起来。得到的MOF薄膜清晰且具反光特性,说明薄膜粗糙度降低。接着通过旋涂引入含有前体的卤化物盐(halide salts),以将Pb-MOF转化为Pe-MOF。使用这种连续的两步沉积技术,可以为Pe-MOF转换机制找到最佳操作窗口,以产生高效性且均匀的发射。
虽然PeNCs寿命短的主要原因被认为是在运行中的组件上施加的电场影响下触发的离子迁移,但仍有其它机制会导致设备性能衰减,包括界面或电化学反应,以及外部因素(湿度和温度)[10,11]。尽管Tsai等人发现,在主动组件运作致使老化后,MOF保护的PeNCs的光致发光出射峰值和FWHM没有受到影响,LED仍然表现出衰退的性能,这说明存在额外的老化机制。作者认为该组件可能受到界面极化的影响。尽管明确地阻止了离子迁移,但界面可能会遭受界面极化,说明需要进一步的设备工程设计。
实现105 cd m-2以上的最大亮度是Tsai等人目前工作中记录的一个重要的里程碑。这是非常出色的且展现出在高亮度的情况下进一步提高器件寿命的希望。当然要将中高亮度级别的设备寿命提高到10000个工作小时以上还有很长的路要走。然而必须注意的是,有机LED(OLED)在20年内达到了所需的使用寿命水平。PeLED研究界在这么短的时间内达到了令人瞩目的进展,对于我们在未来追求中高亮度BT.2020兼容显示器的长期稳定性给予很多的希望。
|
参考资料: |
Vassili Fedotov, “Metal–organic frameworks protect perovskite,”
Nature Photonics volume
15, pages796–797 (2021)
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-021-00898-5
DOI:s41566-021-00898-5
|
|
参考文献: |
[1] Yan, F. et al.
Nano Lett. 18, 3157–3164 (2018)
[2] Kim, Y.-H. et al.
Nat. Photon. 15, 148–155 (2021)
[3] Li, H. et al.
Adv. Mater. 33, 2008820 (2021)
[4] Tsai, H. et al. Nat. Photon. https://doi.org/10.1038/10.1038/s41566-021-00857-0 (2021)
[5] Zhang, C. et al. Nat. Commun.
8, 1138 (2017)
[6] Zhang, Q. et al. J. Solid State Chem. 272, 221–226 (2019)
[7] He, H. et al. Adv. Mater. 31, 1806897 (2019)
[8] Hou, J. et al. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 19434–19449 (2020)
[9] Zhang, C. et al. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 7488–7501 (2021)
[10] Yan, F. & Demir, H. V. Nanoscale 11,
11402–11412 (2019)
[11] Dey, A. et al. ACS Nano 15, 10775–10981 (2021)
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
|