 |
Emitting layer
design of a white organic light-emitting device
Professor Jiun-Haw Lee
Graduate Institute of Photonics and
Optoelectronics, National Taiwan University
台湾大学光电所 李君浩教授
A white organic light-emitting
device (WOLED) based on a
phosphorescent blue and green
emitter combined with red
fluorescent one doped in a
single host is presented. In
such a device, efficient
phosphorescent sensitization
(PS) was achieved from the green
phosphorescent emitter to the
red fluorescent one, which was
directly observed from transient
electroluminescence. An undoped
region was inserted between the
green and blue dopant region to
stabilize the emission spectra.
In this configuration, the main
recombination zone was at the
blue-emitting region, and the
minor one was located at the
green one near the undoped
region. To avoid carrier
trapping, the red fluorescent
emitter with a reasonably high
concentration (0.5%) was doped
away from the minor
recombination zone. That WOLED
exhibited a longer operation
lifetime than the phosphorescent
blue/green device, because the
PS provided a radiative
efficient energy relaxation from
the green phosphorescent emitter
to the red fluorescent one
[published in Curr. Appl. Phys.
11, S183, 2011].
 |
|
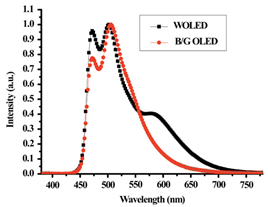
Fig. 1.
Normalized EL spectra of the WOLED and
blue/green OLED. |
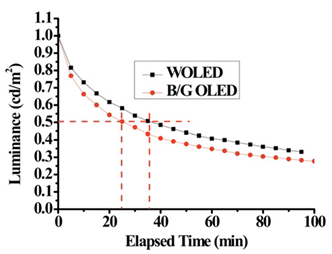 |
|
Fig. 2.
Luminance decay curves of OLEDs. |
Fabrication and
characterization of a micro tunable cat’s eye
retro-reflector
Professor Jui-che Tsai
Graduate Institute of Photonics and
Optoelectronics, National Taiwan University
台湾大学光电所 蔡睿哲教授
We developed a micro tunable
cat’s eye retro-reflector. The
tunability is obtained through
the use of a smart film, a
polymer dispersed liquid crystal
device (PDLC). The cat’s eye
device consists of three
subassemblies, a front-side
focusing unit, the smart film,
and a back-side reflecting unit.
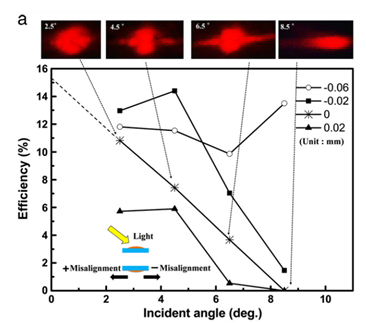
Device characterization,
considering possible fabrication
inaccuracy such as misalignment,
was performed (Fig. 1). The
acceptance angle was measured to
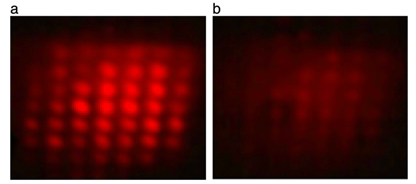
be 9°. Switching of an image
pattern generated by a 2-D array
of such tunable cat’s eye
retro-reflectors was also
demonstrated (Fig. 2). The
tunable cat’s eye
retro-reflectors can be used in
a free-space communication
system, or more specifically, an
optical identification system.
 |
|
Figure 1 |
 |
|
Figure 2 |
© 2011 Elsevier B.V.
K. H. Chao, C. D. Liao, B. J.
Yang, and J. C. Tsai,
“Fabrication and
characterization of a micro
tunable cat’s eye
retro-reflector,” Optics
Communications, Vol. 284,
pp. 5221-5224, Oct. 2011.
|
 |