 |
Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Behaviors of Au Nanorings Monitored with Optical Coherence Tomography
Professor
C. C. (Chih-Chung) Yang's
Laboratory
Graduate Institute of Photonics and
Optoelectronics, National Taiwan University
臺灣大學光電所 楊志忠教授
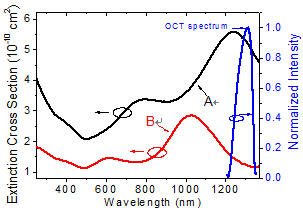
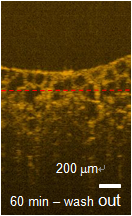
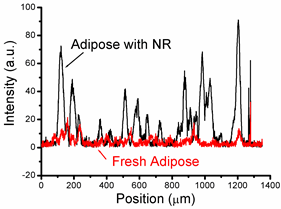
Preparation of a high-concentration Au nanoring (NRI) water solution and its applications to the enhancement of image contrast in optical coherence tomography (OCT) and the generation of photothermal effect in a bio-sample through localized surface plasmon (LSP) resonance are demonstrated. Au NRIs are first fabricated on a sapphire substrate with colloidal lithography and secondary sputtering of Au, and then transferred into water solution through a liftoff process. By controlling the NRI geometry, the LSP dipole resonance wavelength in tissue can cover the spectral range of 1300 nm for OCT scanning of deep tissue penetration. The extinction cross sections of the fabricated Au NRIs in water are estimated to give the levels of 10-10-10-9 cm2 near their LSP resonance wavelengths. The fabricated Au NRIs are then delivered into pig adipose samples for OCT scanning. It is observed that when resonant Au NRIs are delivered into such a sample, LSP resonance-induced Au NRI absorption results in a photothermal effect, making the opaque pig adipose cells transparent. Also, the delivered Au NRIs in the intercellular substance enhance the image contrast of OCT scanning through LSP resonance-enhanced scattering. By continuously OCT scanning a sample, both photothermal and image contrast enhancement effects are observed. However, by continually scanning a sample with a low scan frequency, only the image contrast enhancement effect is observed. Figure 1 shows the SEM image of an Au NRI. Figure 2 shows the extinction spectra of two NRI samples (A and B) obtained through transmission measurement. The major peak of each curve corresponds to the LSP dipole resonance. Figure 3 shows the OCT scanning image of a pig adipose sample with delivered Au NRIs. The adipose cells have become transparent. Figure 4 shows the lateral line-scan profiles of the OCT images of the heated pig adipose samples with and without Au NRIs. Enhanced scattering through LSP resonance of Au NRIs can be seen.
|
 |
 |
|
Fig. 1 SEM image of an Au NRI. |
Fig. 2 Extinction spectra of Au NRIs (samples A and B). |
|
 |
 |
|
Fig. 3 OCT image of a pig adipose sample with Au NRIs. |
Fig. 4 Lateral line-scan profiles of the OCT images of the heated pig adipose samples with and without Au NRIs. |
Numerical Synthesis of Metallic Nanostructures for
Enhancing the Emission of a Dipole
through Surface Plasmon Coupling
Professor Yean-Woei
Kiang's Laboratory
Graduate Institute of Photonics and
Optoelectronics, National Taiwan
University
臺灣大學光電所 江衍偉教授
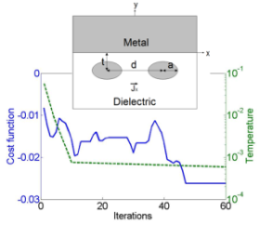
In this study, we numerically synthesize a two-dimensional metallic nanostructure consisting of a Au half-space and two separate Ag elliptical cylinders by the simulated annealing (SA) method. The simulated nanostructure is so designed that the surface plasmon polariton (SPP) and the localized surface plasmon (LSP) are simultaneously excited at their common resonant wavelength (535 nm), leading to the enhancement of emission of a nearby dipole source. This enhancement effect is more significant than that of the case where only one of SPP and LSP is excited. In numerically synthesizing a metallic nanostructure, we try to maximize both the downward emission (in the direction away from the metallic structure) and the emission efficiency. A cost function is defined as some combination of the downward emission and the emission efficiency. We adjust the simulated structure by SA to minimize the cost function at a designated resonant wavelength, and calculate and analyze the spectra of downward emission and emission efficiency for the optimal structure. Other structures are also investigated for comparison. From numerical simulations, it is demonstrated that the enhancement of dipole emission is better for optimization at wavelength 535 nm than at other wavelengths. Note that the downward emission and the emission efficiency can reach maxima almost simultaneously when the SPP and the LSP couple effectively at a common resonant wavelength. This implies that the lighting efficiency of green light-emitting diodes (LEDs) can be increased by the coupling effect at a common resonant wavelength of SPP and LSP.
|
 |
 |
|
Fig. 1 Variation of cost function in the iteration process. The solid curve represents the cost function and the dashed curve represents the chosen temperature distribution used in the SA process. The synthetic metallic nanostructure is shown schematically in the insert. An x-oriented dipole, denoted by an arrow and labeled by Jx, is located at (x,
y) = (0, -h). The metal-dielectric flat interface is at
y = 0.
|
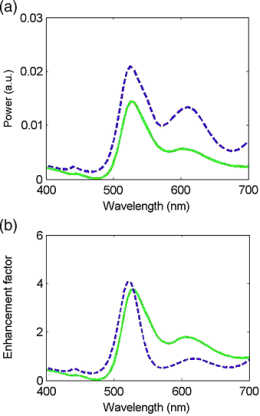
Fig. 2 Spectra of (a) total emission (dashed curve) and downward emission (solid curve), and (b) enhancement factor of total emission (dashed curve) and downward emission (solid curve) for structure A (structure parameters:
a = 12 nm, d = 60 nm,
t = 10 nm, h = 21 nm).
|
|
 |