|
A Novel
Boundary-Confined Method for High
Numerical Aperture Microlens Arrays
Fabrication
Professor
Guo-Dung John Su
Graduate Institute of Photonics and
Optoelectronics, National Taiwan
University
臺灣大學光電所 蘇國棟教授
We present
a technique to improve microlens arrays
(MLAs) uniformity after the thermal
reflow process. Microlens arrays (MLAs)
usually form a layered structure in
application-specific optical systems,
such as backlight modules for liquid
crystal displays (LCD), extraction
improvement film for layered light
emitting devices, wavefront sensors,
image recorders, and a focusing
component in the optical communication
devices. It is hard to make small lenses
and large arrays by traditional
machining. Although several methods are
proposed to replace the traditional
machining, thermal reflow process is
widely used to fabricate MLAs.
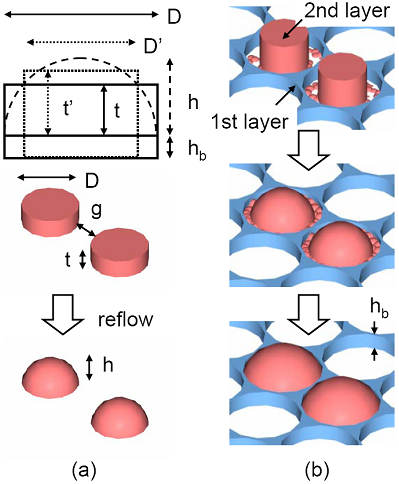
To
overcome this difficulty, a novel method
is proposed and demonstrated in this
paper. It is called the
boundary-confined method. A boundary
between each PR cylinder is defined
first by a thin negative tone PR. A
thermal reflowing of a 2nd
thick PR is halted at the boundary, as
shown in Fig. 1. The uniformity can be
improved without the cling phenomenon.
Besides, the boundary is narrow and only
a small amount of fill-factor is
sacrificed. The height of the microlens
is adjustable by the different diameter
of PR cylinders inside the same boundary
wall. We achieved high uniformity and
high-NA (numerical aperture)
simultaneously without sacrificing
fill-factor too much. In order to
improve fill-factor, residual PR (photoresist)
between the photoresist cylinders are
used to make photoresist flow outward in
standard thermal reflow processes. PR
cylinders, however, merge together
easily due to an inexact reflow time and
temperature distribution. This results
in low uniformity and small lens height
or low-NA. We proposed a
boundary-confined method to pattern thin
PR holes to prevent PR microlenses from
merging together even after a long
reflow time. Thick PR cylinders are
patterned inside thin PR holes served as
boundaries. PR microlenses are formed
after reflowing the thick photoresist
cylinders. Both the uniformity and the
height of microlens can be well
controlled. Besides, the fill-factor is
high due to the high resolution at thin
photoresist layer in photolithography.
Our results show that the microlens is
approximately a hemispherical profile.
The gap between microlenses with 48
mm
diameter in hexagonal arrangement is 2
mm and the height of microlens is 22
mm,
as shown in Fig. 2. This work is also
patterned under US 7,713,453 B2.
|
 |
|
Figure 1.
Schematic drawing of PR reflow by
boundary-confined method. |
|
Figure 2. The
fabrication process sequence, and
(a) PR microlens and SU-8 boundary,
(b) PDMS mold captured by a
microscope, (c) UV gel MLAs after
releasing from PDMS mold. |
|