 |
|
 |
| |
发行人:黄建璋所长 编辑委员:曾雪峰教授 主编:林筱文 发行日期:2019.10.30 |
| |
|
 |
|
 本所陈奕君教授指导许书铭博士生荣获「European Materials Research Society 2019 Fall Meeting (欧洲材料研究学会2019秋季会议) Graduate Student Award」,特此恭贺!
本所陈奕君教授指导许书铭博士生荣获「European Materials Research Society 2019 Fall Meeting (欧洲材料研究学会2019秋季会议) Graduate Student Award」,特此恭贺!
|
获奖同学
|
指导教授 |
论文题目 |
|
许书铭 |
陈奕君教授 |
Complementary Inverters Composed of Oxide Thin-Film Transistors |
 本所林恭如教授指导吴伟立硕士生荣获「中国电机工程学会2019年度青年论文奖第三名」,特此恭贺!
本所林恭如教授指导吴伟立硕士生荣获「中国电机工程学会2019年度青年论文奖第三名」,特此恭贺!
|
获奖同学
|
指导教授 |
论文题目 |
|
吴伟立 |
林恭如教授 |
预补偿分频多任务算法于高位率数据中心光传输 |
|
|
 |
|
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
~ The
4th International Conference on BioPhotonics;
ICB 2019 ~
(September 15~18, 2019, at Barry Lam Hall, NTU)
The 4th International Conference on BioPhotonics (ICB; http://icb2019.ntu.edu.tw/) was held at the Barry Lam Hall of the National Taiwan University during Sept. 15–18, 2019. More than 150 scholars and graduate students were registered from more than 10 countries. The goal of the ICB is to have technical exchanges and networking among the leading academics worldwide. Emergent areas that have the potential to significantly benefit our future life, such as precision medicine, cell/immune-therapy, liquid biopsy, optical biopsy, artificial intelligence on biomedicine, were addressed in the 42 papers during the ICB 2019.
Many renowned speakers shared their latest achievements and insights on the future of research in biophotonics ranging from life science to clinical applications. Professor Xingde Li, Johns Hopkins University, U.S.A. addressed OCT and endomicroscopy towards visualization of histology; Prof. Marcus Sauer, University of Wuerzburg, Germany addressed single-molecule sensitive super-resolution microscopy, and Prof. Ann-Shyn Chiang, National Tsing Hua University addressed mapping the Drosophila engram.
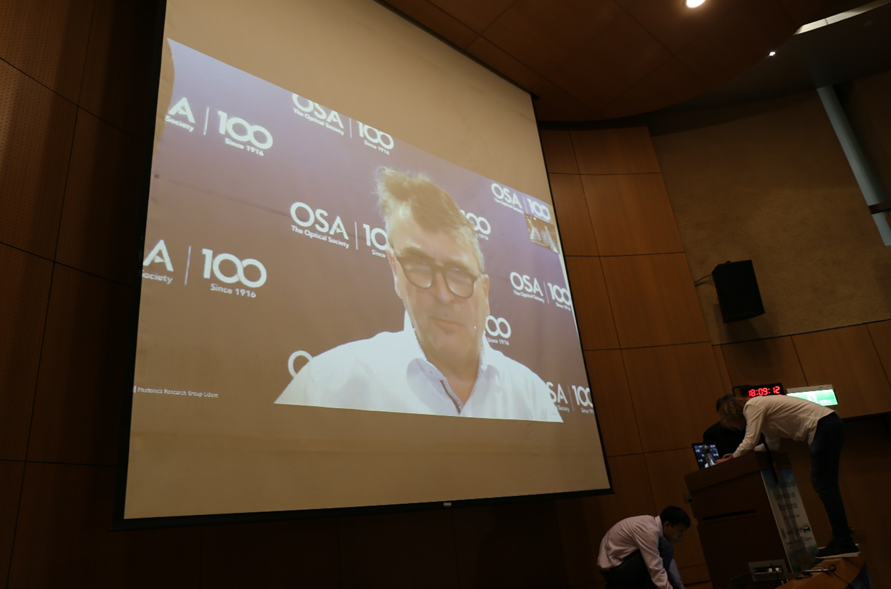
This year, we had a teleconference session, which was delivered by Prof. Roel Baets of the Ghent University, Belgium. He delivered the talk while he was in Washington DC, US. It was a good experience to witness the power of photonics technology by reducing the physical transportation in response to global warming.
The ICB 2019 was jointly sponsored by the National Taiwan University, the Taipei and Italy Chapters of IEEE Photonics Society, IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, and Taiwan Photonics Society. The Organizers also appreciate the funding support by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan as well as the industrial sponsorships from Apollo Medical Optics and Crystalvue Medical Corporation.
|
 |
|
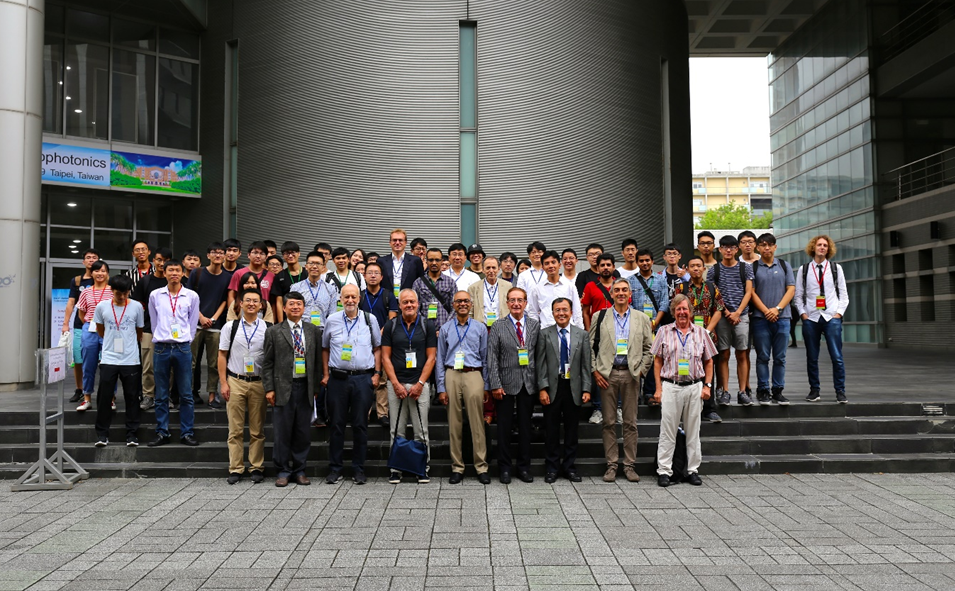
Fig. 1
Group photo of the ICB 2019 participants. |
|
 |
 |
|
Fig. 2 Welcome address by Prof. JianJang Huang, Chairman, Graduate Institute of Photonics and Optoelectronics, National Taiwan University. |
Fig. 3 Plenary speech by Prof. Xingde Li, Johns Hopkins University, USA. |
|
 |
 |
|
Fig. 4 Teleconference by Prof. Roel Baets, Ghent University, Belgium. |
Fig. 5 The IAC Chair (Prof. Silvano Donati, left) and TPC Chair (Prof. Fu-Jen Kao, right). |
|
 |
 |
|
Fig. 6 Lunch time at the Barry Lam Hall. |
Fig. 7 The poster session of ICB 2019. |
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
| |
|
 |
Development of Anti-UV Structures for OLED Displays
Professor Chung-Chih Wu
Graduate Institute of Photonics and
Optoelectronics, National Taiwan University
台湾大学光电所 吴忠帜教授
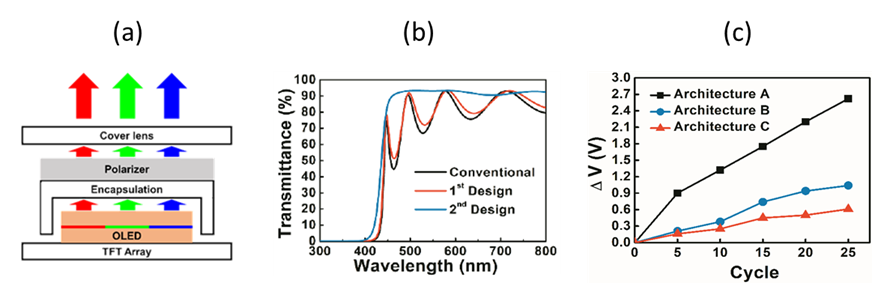
Although OLED displays are penetrating into wider applications in consumer electronics due to their high efficiency, high contrast, and good color gamut etc., their extension to outdoor applications (e.g., wearable, vehicular, signage applications etc.) is still facing significant reliability challenges. One major issue is their weak resistance against the UV-light induced degradation; the ultraviolet light (UV-light,
λ<400nm) and high energy visible light (HEV-light, 400 <
λ
< 450 nm) in sunlight would significantly degrade OLEDs and much shorten display lifetimes. Thus, an effective anti-UV technique, that can protect OLEDs from UV/HEV damage and meanwhile maintain display performance, is strongly required. Here we report the development of effective anti-UV/HEV, high-transmittance, high-image-quality structures for OLED display panels based on carefully designed optical thin-film structures composed of more robust inorganic UV-absorbing and dielectric materials, instead of polymer/organic materials that may suffer yellowing by UV radiation.
|
|
|
Fig. 1.(a) Typical OLED panel structure. (b) Transmittance spectra of different anti-UV thin film structures. (c) Voltage shifts (ΔV) of test samples under a same current density after repeated solar soaking test cycles. |
|
 |
| |
|
|
|
 |
|
| |
|
 |
论文题目:第一原理新颖信道与铁电材料研究及后端依时性介电崩溃之可靠度模型
姓名:陈品翔 指导教授:刘致为教授
| 摘要 |
|
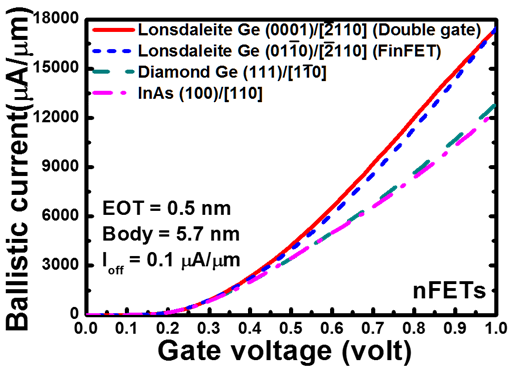
当晶体管尺寸持续微缩后,使用具有高迁移率的信道材料来增加驱动电流或降低能耗是未来半导体组件发展的方向之一。在论文的第一部分将会针对锗之同素异形体,蓝丝黛尔锗(lonsdaleite Ge)进行特性分析,包含其能带结构、等效质量、弹道电流以及应变响应等皆会详细分析。具有稳定结构之蓝丝黛尔锗预期能有效提升组件表现而不改变其材料构成,而其直接能隙之特性亦利于用于光电组件之应用。
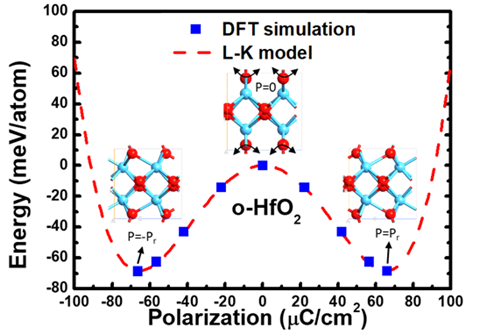
组件在设计上,其截止电流须保持相同或者更低以保持低静态功率,与此同时,亦须保持高的操作电流,因此,尽可能降低组件之次臨界摆幅十分重要。加入铁电材料到闸极堆栈的负电容场效应晶体管,其利用铁电材料内之偶极矩随偏压改变时改变极化方向之特性,将能使次臨界摆幅有效克服传统织极限值。在论文的第二部分,将以第一原理进行正交结构氧化锆铪(HfZrO2)之特性分析,利用其能量与极化之关系确定其铁电特性。以及,利用分子动力学模型计算其动态反应。除此之外,亦会探讨应变对其造成之影响。
在组件尺寸不断微缩的过程中,其失效机制亦是十分重要的一环,故在此论文中亦会探讨后段制程(BEOL)中介电层的崩溃机制,造成介电层崩溃的原因可能为施加电场或是漏电流造成,如何精确的了解其机制并藉此预测其可靠度变化是十分重要的。藉由后段制程中介电层之漏电流以及时依性介电层崩溃之数据,建立可靠度的模型,藉以进行组件于正常使用状态下之可靠度预测。
|
|
|
图一、蓝丝黛尔锗具有较高之弹道电流 |
|
|
|
图二、正交结构氧化锆铪具有铁电材料之能量特性 |
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
|