 |
|
 |
| |
发行人:林恭如所长 编辑委员:吴肇欣教授 主编:林筱文 发行日期:2018.07.30 |
| |
|
 |
Ultrahigh Responsivity and Superior Sensitivity Graphene-semiconducting Light Absorber Hybrid Phototransistors
Professor Chih-I Wu
Graduate Institute of Photonics and
Optoelectronics, National Taiwan University
台湾大学光电所 吴志毅教授
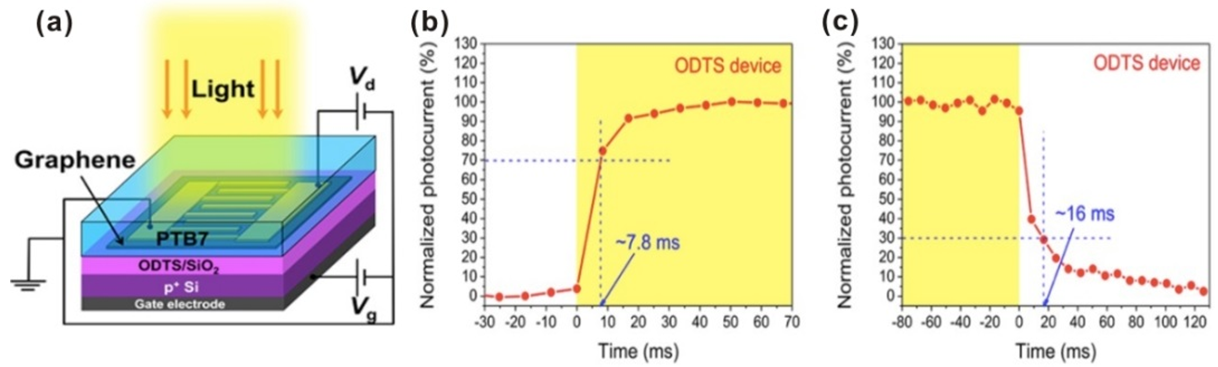
Graphene−semiconducting light absorber hybrid photodetectors have attracted increasing attention because of their ultrahigh photoconductive gain and superior sensitivity. However, most graphene based hybrid photodetectors reported previously have shown a relatively long response time caused by numerous long-lived traps in these hybrid systems, which greatly restricts device speed. In our studies, we found graphene/light-harvesting materials (such as thieno[3,4-b]thiophene/ benzodithiophene polymer (PTB7) and Bismuth(III) iodide (BiI3)) hybrid photodetectors have high responsivity and short photocurrent response time. Figure 1 shows the graphene-PTB7 hybrid photodetectors fabricated on self-assembled-monolayer functionalized SiO2 substrates with a maximum responsivity of ~ 1.8 ×105 A/W and a relatively short photocurrent response time of ~ 7.8 ms.
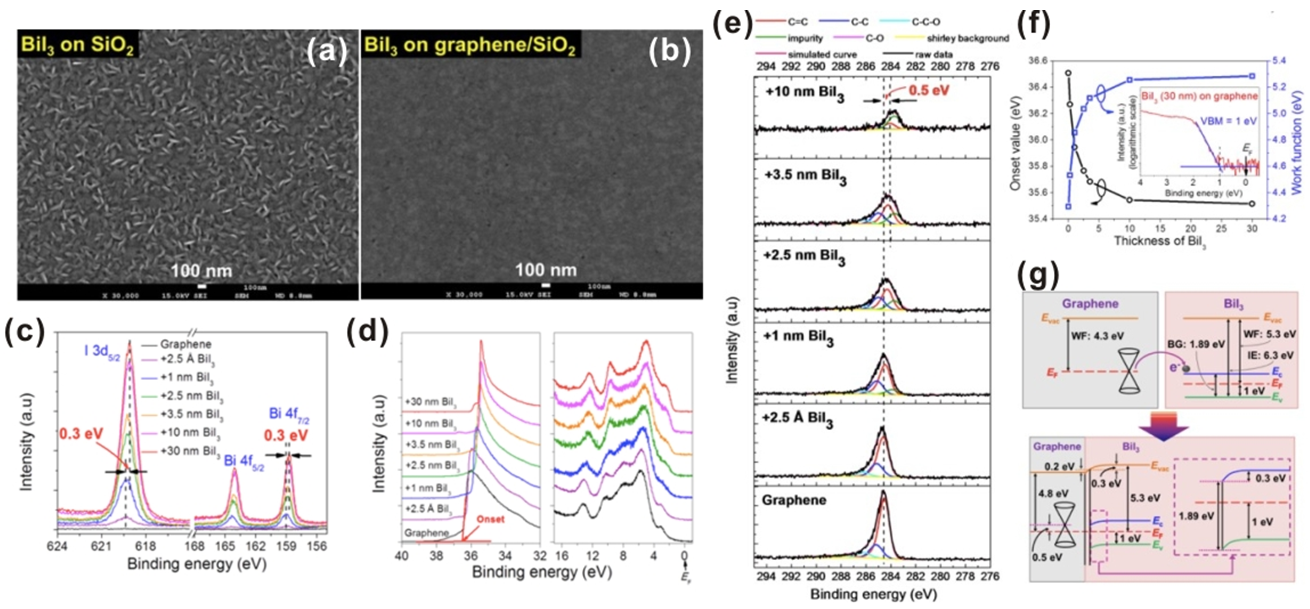
Besides, the graphene/BiI3 vertical heterostructure phototransistors also have a maximum responsivity of about 6×106 A/W , EQEs of up to 106 % in the visible light region, relatively short photocurrent response times of ~ 8 ms, and detectivity of 7×1014 Jones under the SNL condition. Compared to BiI3 on bare SiO2 substrates, the thermally evaporated BiI3 films on graphene sheets possessed nearly flatter morphologies and remarkably better crystallinities because of the weak van der Waals interactions between graphene and BiI3. In Figure 2, the photoemission spectra of graphene/BiI3 heterojunctions also manifest the evidence that no chemical interactions occur between graphene and BiI3, resulting in the van der Waals epitaxial growth. The measured band bending consistently illustrates that photo-induced charge transfer occurs at the graphene/BiI3 interface. The high-quality crystal growth of the layered metal halide BiI3 could make graphene/BiI3 heterostructures a promising building block for high-performance optoelectronic applications.
|
|
|
Figure 1. (a) Schematic illustration of a graphene−PTB7 hybrid photodetector (b) Rise time and (c) fall time of the device |
|
|
|
Figure 2. SEM images of 50 nm thermally evaporated BiI3 film on (a) SiO2 and (b) graphene/SiO2. Photoemission spectra of graphene with incrementally increased BiI3 film thickness. (c) XPS spectra of I3d5/2 and Bi4f. (d) UPS spectra for SEC (left) and VB (right) regions, respectively. (e) C1s
peak-fitting XPS spectra. (f) The onset values of the SEC spectra (black dot) and the corresponding WFs (blue dot) as a function of the BiI3 thickness. The inset shows the VB maximum position of bulk BiI3. (g) Individual electronic structures of pristine graphene and BiI3. The energy level alignment and band bending at the graphene/BiI3 heterojunction are depicted in the bottom panel. |
Reference :
1. Chang P. H., Tsai Y.C., Shen S. W., Liu S.Y., Huang K. Y., Li C. S. Chang, H. P., and Wu C. I., Highly Sensitive Graphene−Semiconducting Polymer Hybrid Photodetectors
with Millisecond Response Time,
ACS Photonics
2017,
4, 2335−2344
2.
Chang P. H., Li C. S., Fu F. Y, Huang K. Y, Chou A. S.,
and Wu C. I., Ultrasensitive Photoresponsive Devices Based on Graphene/BiI3 van
der Waals Epitaxial Heterostructures,
Advanced Functional Materials
2018,
28, 1800179
|
 |
| |
|
|
|
 |
|
| |
|
 |
论文题目:全域式光学同调断层扫描仪于皮肤组织之量化参数研究
姓名:张家凯 指导教授:黄升龙教授
| 摘要 |
|
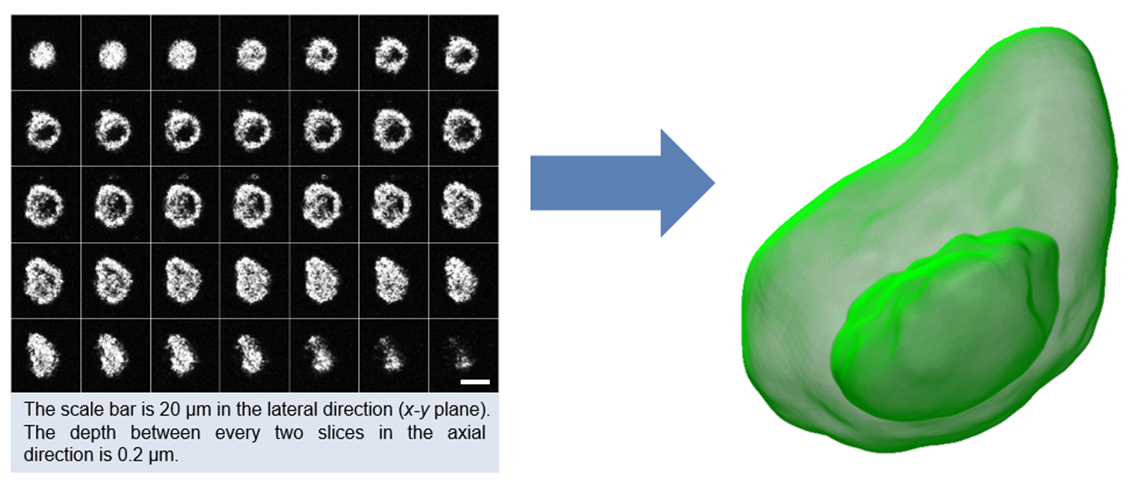
以往的生物细胞分析是透过二维影像来建立量化信息,我们通过分辨率为横向0.8 µm,纵向0.9 µm的全域式同调断层扫描(FF-OCT)系统,获取三维断层扫描立体影像,以三维立体信息来分析,可以得到较全面的信息。本研究开发随机射线取样(Random rayburst sampling; RRBS)框架,用于检测三维空间中的细胞核与细胞膜的边界,从而进行单细胞的量化分析,计算出单细胞的体积核质比(nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio)与细胞立体形貌(图一)。RRBS对噪声不敏感,不同随机选择的RRBS计算所得到的体积核质比之间的相对标准偏差为2%。以荧光共焦显微镜做验证,RRBS算法于体积核质比的误差仅为1%。为了提升计算效率,本研究使用图形处理器(Graphics processing unit; GPU)的并行计算,若使用Nvidia的GTX 1080图形处理器,于三维双边滤波器之计算可以得到280倍的速度提升。
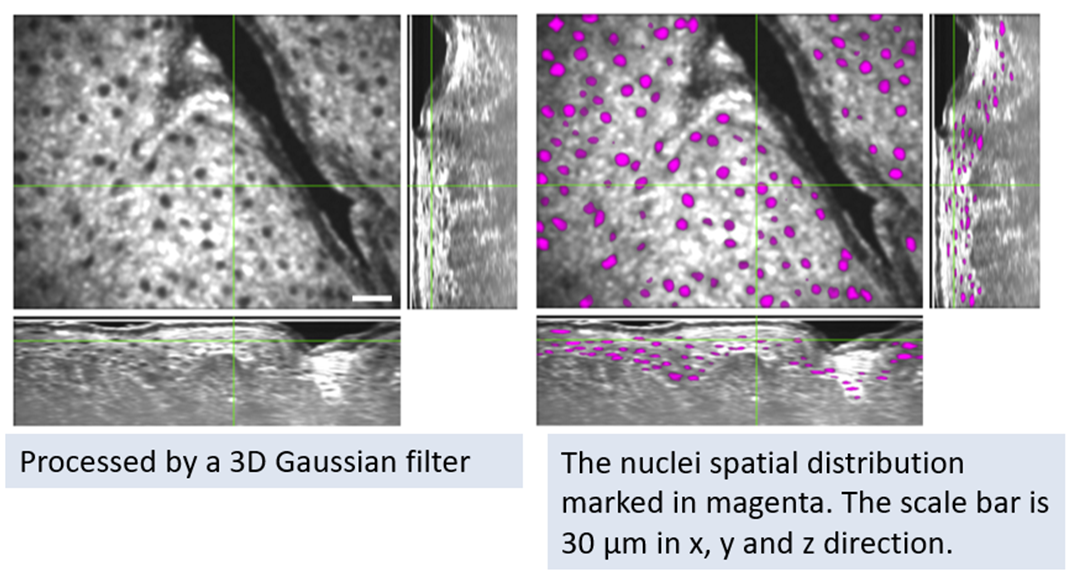
RRBS框架也可应用于活体皮肤组织的量化分析(图二)。角质形成细胞(Keratinocytes)之细胞核的体积由颗粒层(Stratum granulosum)到基底层(Stratum basale)逐渐变小,结合FF-OCT的快速三维断层扫描与RRBS框架可以提取位于表皮层(Epidermis)不同深度的角质形成细胞之细胞核的三维形态特征,进而对活体皮肤进行量化分析,角质形成细胞核在基底层的平均纵向和横向直径分别为5.1±0.34和7.2±0.74 µm,RRBS框架与本实验室的细胞等级高分辨率FF-OCT搭配,有潜力作为皮肤之疾病与癌症的早期诊断的有效方法。
 |
|
图一 |
 |
|
图二 |
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
|
| |
|
 |
— 资料提供:影像显示科技知识平台 (DTKP, Display Technology
Knowledge Platform) —
—
整理:林晃岩教授、孟庆棠 —
偏振特性决定全球定位
海洋动物能否使用偏振敏感视觉作为在水底的自然全球定位系统?根据最近由美国和澳大利亚的计算器科学家、海洋生物学家和物理学家进行的一项研究(Sci. Adv.
4, eaao6841; 2018),结果是此项功能是可行的。该团队的实验数据和分析显示,太阳的位置(朝向和仰角)可以根据水下的光线偏振模式来确定,因此如果观测者了解时间和日期,则可以推断出他们在全球的位置。这种水底偏振图案是藉由日光的折射和散射的组合而产生的。特别的是,穿过天空/海洋边界的空气/水界面的太阳光在入射和折射光线的平面内以其特征产生偏振。同时,部分散射使与该平面垂直的光产生偏振。这些组合之效果随着太阳位置而变产生许多变化的偏振模式。
为了测试他们的假设,该团队建立了一个水下偏振敏感相机,如图一(A)所示。其中由平行铝奈米线所制成的偏振滤波器,以0°、45°、90°和135°的角度对准,并沉积在2兆像素的感光组件上,如图一(B)所示。这种摆置允许摄像机捕捉光强度,部分偏振和偏振角影像,并模仿螳螂虾的视觉系统。然后使用相机在世界各地不同的地点(澳大利亚、夏威夷、佛罗里达和芬兰)、不同的水深(2-20米)以及从日出到日落中不同的时间来拍摄实验数据。其结果显示使用这种系统的导航是可能的,其每行进1公里的误差约为6米。
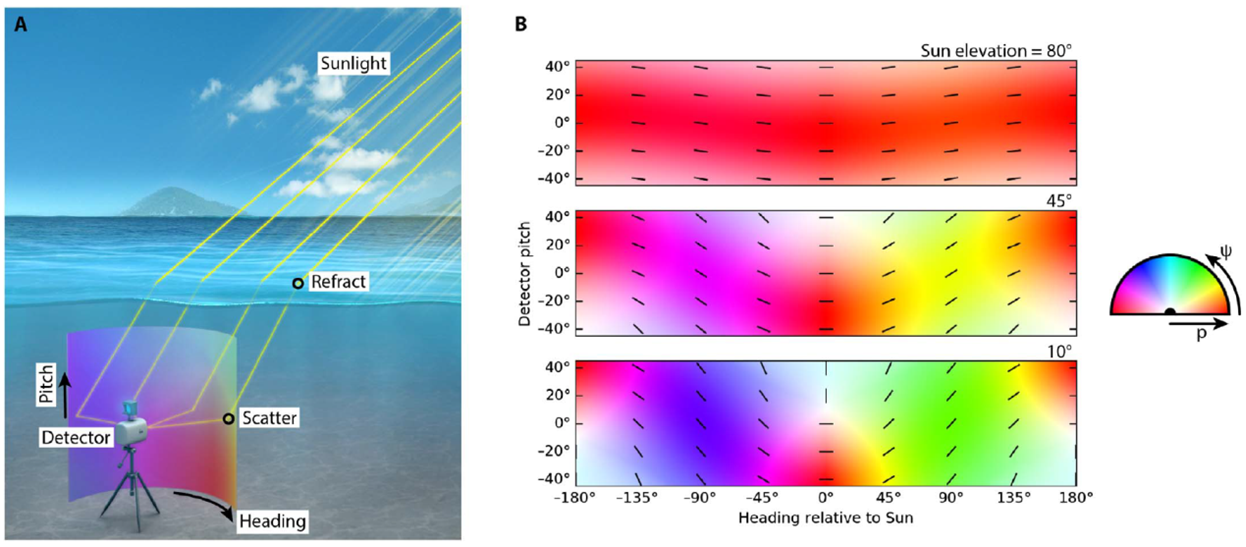 |
|
图一、水底极化系统示意图。(A) 圆柱体显示检测器观察到的偏振态。(B) 单一散射模型可预测的偏振态在太阳升起高于水平面10°、45°和80°(见右图)。为了清楚起见,以偏振角为方向的线覆盖在图上。偏振的中性点发生于散射之偏振状态抵消折射之偏振状态时
。 |
因为几种海洋动物具有极化敏感的视觉,因此它们可能将其视觉用作指南针,应用于长途水底导航和地理定位。而此已经被许多陆生节肢动物,如:蚂蚁、蜜蜂、甲虫和蜘蛛,其使用光的极化作为导航辅助已获证实。尽管该团队的测量只发生在四个不同的全球地点(如图二),但他们认为依据海水一致性之特性代表该方法具有普遍的适用性。
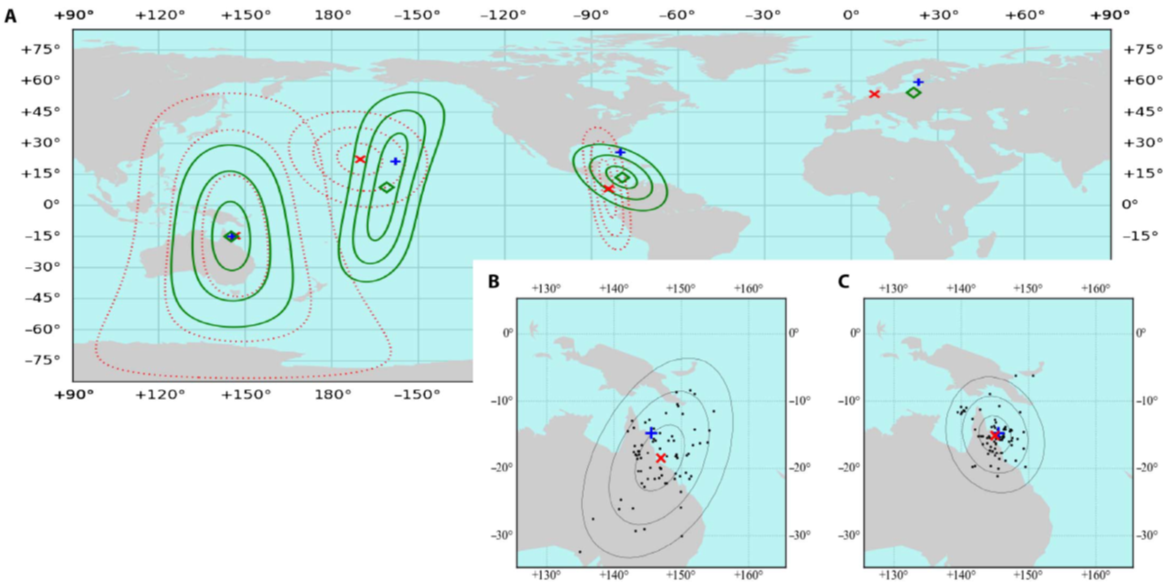 |
|
图二、(A) 澳大利亚、夏威夷、佛罗里达和芬兰四个测试地点的位置评估。蓝色十字为测试点位置;红色叉叉与虚线为单一散射评估的结果;绿色菱形与曲线为使用k-最近相邻回归法评估的结果。(B) 单一散射评估的结果。(C) k-最近相邻回归法评估的结果。 |
|
参考资料: |
[1] Oliver Graydon, “Global position by polarization,” Nature Photonics, volume 12, page 318 (2018)
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41566-018-0187-3
DOI: 10.1038/s41566-018-0187-3
[2] Samuel B. Powell, Roman Garnett, Justin Marshall, Charbel Rizk, Viktor Gruev, “Contact Lenses for Color Blindness,” Sci Adv, 4 (4), eaao6841(2018).
http://advances.sciencemag.org/content/4/4/eaao6841
DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aao6841
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
|