|
Surface
Tension and Concentration Measurement of
Sub-mL Solution Using a Cantilever-Based
Optical Gauging System
Professor Jui-che Tsai
Graduate Institute of Photonics and
Optoelectronics, National Taiwan
University
臺灣大學光電所 蔡睿哲教授
A
cantilever sensor integrated with an
on-tip micro spherical reflecting mirror
(MSRM) exhibits a larger optical beam
displacement than a conventional one,
i.e., the system sensitivity/responsivity
is enhanced. In our study, it is
employed as a surface tension and
concentration gauge that only requires
0.5
mL of solution.
The
MSRM-integrated cantilever is first set
above a sodium chloride-water droplet
carried by a glass substrate, and then
the droplet is moved up gradually. Once
the cantilever is touched by the
droplet, it is pulled and bent down as
the droplet reshapes. The cantilever
deformation amount is related to the
surface tension of the solution, which
increases with the molar concentration
of sodium chloride. According to our
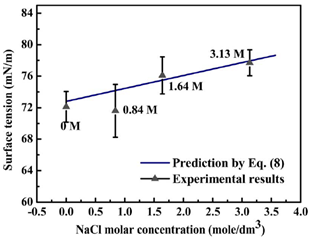
experiments, the surface tension varies
from 72.1 to 77.7 mN/m as the molar
concentration of sodium chloride in
water increases from 0 to 3.13 M (Fig.
1). Therefore, by measuring the bending
amount of the cantilever, the surface
tension as well as the concentration of
the NaCl-water solution can be
determined. We also perform the
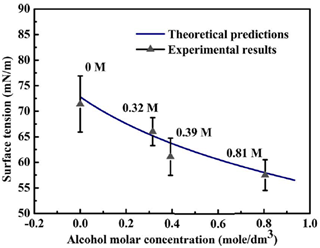
experiments on the alcohol
(ethanol)-water mixture, whose surface
tension, conversely, reduces from 71.4
to 57.5 mN/m as the alcohol molar
concentration increases from 0 to 0.81 M
(Fig. 2).
|
 |
|
Fig. 1 |
|
 |
|
Fig. 2 |
© 2010
IEEE
C. D.
Liao, K. H. Chao, and J. C. Tsai,
“Surface tension and concentration
measurement of sub-mL solution using a
cantilever-based optical gauging
system,” IEEE Journal of Quantum
Electronics, Vol. 46, No. 9, pp.
1268-1274, September 2010.
Arbitrary-Order Interface Conditions for
Slab Structures and Their Applications
in Waveguide Analysis
Professor Yih-Peng Chiou
Graduate Institute of
Photonics and Optoelectronics, National
Taiwan University
臺灣大學光電所 邱奕鵬教授
Convergence of truncation
error is one of critical factors in
finite-difference simulation. Since
step-index structure is a common feature
in recent photonic devices design,
traditional formulation based on
graded-index (GI) and index averaging
(IA) scheme cannot accurately model
field behavior near abrupt interfaces
between different materials. We derive
generalized interface conditions of
arbitrary orders combined with Taylor
series expansion in homogeneous region
for TE and TM mode calculation of
step-index waveguide. We also adopt
generalized Douglas (GD) scheme for
further convergence order without
demanding more reference points.
We model a
multiple-quantum-well (MQW) waveguides
with 56 barriers and 55 wells as an
assessment. Refractive indices of
cladding, barrier, and well are 3.2224,
3.2874, and 3.3704, respectively. Widths
of each barrier and well are 12nm and
7nm, respectively. The relative
propagation constant error of
fundamental TE and TM modes illustrated
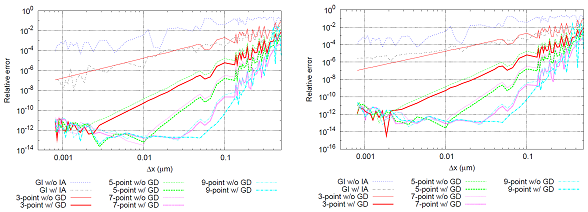
in Fig. 2
shows that our proposed scheme using (2N+1)-point
without GD yields convergence between
O(h2N-1) and O(h2N),
or O(h2N+1) and O(h2N+2)
if GD is adopted. The high-order
convergence can greatly reduce
computation effort of waveguide
analysis. Formulation can also be
applied to other simulation methods such
as beam propagation method.
|
 |
|
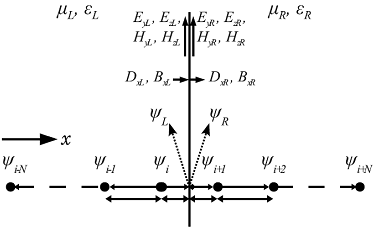
Fig. 1 Illustration of
field continuity and sample points. |
|
 |
|
(a)
(b)
Fig. 2 Relative propagation constant
error of fundamental (a) TE and (b) TM
modes. |
Reference: Y.-P. Chiou and C.-H. Du,
OSA Optics Express, Vol. 18, No. 5,
pp. 4088-4102, Mar. 2010.
|